8-OH-DPAT
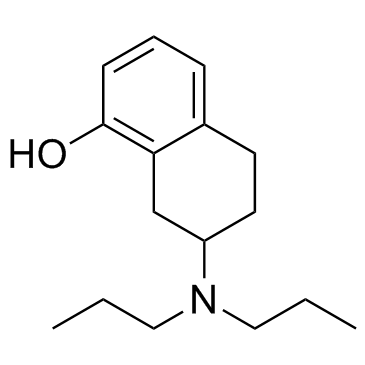
8-OH-DPAT结构式

|
常用名 | 8-OH-DPAT | 英文名 | 8-OH-DPAT |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS号 | 78950-78-4 | 分子量 | 247.37600 | |
| 密度 | N/A | 沸点 | 372.5ºC at 760 mmHg | |
| 分子式 | C16H25NO | 熔点 | N/A | |
| MSDS | 美版 | 闪点 | 168.2ºC |
|
Serotonin 5-HT1A receptor in infancy-onset aggression: comparison with genetically defined aggression in adult rats.
Behav. Brain Res. 243 , 97-101, (2013) Antisocial aggressive behavior in adolescents represents growing clinical and social problem. Previously the implication of 5-HT1A receptor in the regulation of fear-induced aggression was shown. Here, the involvement of 5-HT1A receptor in infancy-onset genet... |
|
|
Unilateral lesion of the nigrostriatal pathway decreases the response of GABA interneurons in the dorsal raphe nucleus to 5-HT(1A) receptor stimulation in the rat.
Neurochem. Int. 61(8) , 1344-56, (2012) This study examined the firing rate and pattern of electrophysiologically and chemically identified GABA interneurons in the dorsal raphe nucleus (DRN), and role of 5-HT(1A) receptor agonist 8-OH-DPAT and the medial prefrontal cortex (mPFC) in the firing acti... |
|
|
Electrophysiological and pharmacological properties of GABAergic cells in the dorsal raphe nucleus.
J. Physiol. Sci. 63(2) , 147-54, (2013) The dorsal raphe nucleus (DRN) is the origin of the central serotonin [5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT)] system and plays an important role in the regulation of many physiological functions such as sleep/arousal, food intake and mood. In order to understand the reg... |
|
|
The cyclooxygenase and nitric oxide synthesis/pathways mediate the inhibitory serotonergic response to the pressor effect elicited by sympathetic stimulation in long-term diabetic pithed rats.
Pharmacology 90(3-4) , 169-76, (2012) We investigated the mechanisms involved in the 5-hydroxytriptaminergic inhibitory action on the pressor responses elicited by sympathostimulation in long-term-diabetic pithed rats. Diabetes was induced in rats by alloxan administration. Eight weeks later, the... |
|
|
5-HT(1A) receptor binding in the dorsal raphe nucleus is implicated in the anxiolytic-like effects of Cinnamomum cassia.
Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 103(2) , 367-72, (2012) Previously we reported that the 50% EtOH extract of Cinnamomum cassia (C. cassia) possesses anxiolytic-like activity in the mouse elevated plus maze (EPM) test. This activity was blocked by the 5-HT(1A) receptor antagonist, WAY 100635. Therefore, in order to ... |
|
|
Targeting melanocyte and melanoma stem cells by 8-hydroxy-2-dipropylaminotetralin.
Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 563 , 71-8, (2014) Monobenzyl ether of hydroquinone (MBEH) is cytotoxic towards melanocytes. Its treatment efficacy is limited by an inability to eradicate stem cells. By contrast, 8-hydroxy-N,N-dipropyl-2-aminotetralin (8-DPAT) affects melanocyte stem cell survival. MBEH and 8... |
|
|
[Analysis of 8-OH-DPAT and NAN-190 effects in young prenatally stressed rats under experimental estrogen deficiency conditions].
Eksp. Klin. Farmakol. 75(7) , 11-4, (2012) The present work was aimed at a comparative investigation of the effects of chronic administration of the 5-HT1A receptor agonist 8-OH-DPAT (0.05 mg/kg, s.c.) and 5-HT1A receptors antagonist NAN-190 (0.1 mg/kg, i.p.) for 14 days on anxiety-like behavior in pr... |
|
|
Quinpirole and 8-OH-DPAT induce compulsive checking behavior in male rats by acting on different functional parts of an OCD neurocircuit.
Behav. Pharmacol. 24(1) , 65-73, (2013) This study investigated whether the serotonin 5-HT1A receptor agonist 8-hydroxy-2-(di-n-propylamino) tetralin (8-OH-DPAT) can induce compulsive checking in a large open field, as does the dopamine D2/D3 receptor agonist quinpirole. To induce compulsive checki... |
|
|
Striatal glutamate release in L-DOPA-induced dyskinetic animals.
PLoS ONE 8(2) , e55706, (2013) L-DOPA-induced dyskinesia is a common side effect developed after chronic treatment with 3,4-dihydroxyphenyl-l-alanine (l-DOPA) in Parkinson's disease. The biological mechanisms behind this side effect are not fully comprehended although involvement of dopami... |
|
|
Association with reward negatively modulates short latency phasic conditioned responses of dorsal raphe nucleus neurons in freely moving rats.
J. Neurosci. 33(11) , 5065-78, (2013) The dorsal raphe nucleus (DRN) is implicated in mood regulation, control of impulsive behavior, and in processing aversive and reward-related signals. DRN neurons show phasic responses to sensory stimuli, but whether association with reward modulates these re... |