1-甲基-L-组氨酸
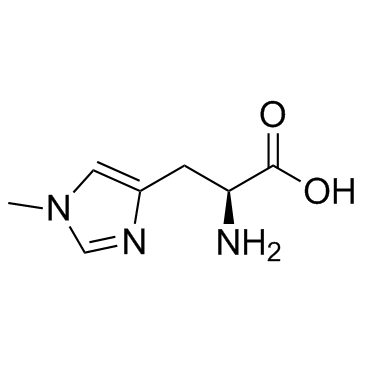
1-甲基-L-组氨酸结构式

|
常用名 | 1-甲基-L-组氨酸 | 英文名 | 1-Methyl-L-histidine |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS号 | 332-80-9 | 分子量 | 169.181 | |
| 密度 | 1.4±0.1 g/cm3 | 沸点 | 415.0±35.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| 分子式 | C7H11N3O2 | 熔点 | ~240 °C (dec.)(lit.) | |
| MSDS | 美版 | 闪点 | 204.8±25.9 °C |
|
Development of High-purity Certified Reference Materials for 17 Proteinogenic Amino Acids by Traceable Titration Methods.
Anal. Sci. 31 , 805-14, (2015) To ensure the reliability of amino acid analyses, the National Metrology Institute of Japan of the National Institute of Advanced Industrial Science and Technology (NMIJ/AIST) has developed high-purity certified reference materials (CRMs) for 17 proteinogenic... |
|
|
Use of high-resolution proton nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy for rapid multi-component analysis of urine.
Clin. Chem. 30(3) , 426-32, (1984) Numerous low-Mr metabolites--including creatinine, citrate, hippurate, glucose, ketone bodies, and various amino acids--have been identified in 400- and 500-MHz proton nuclear magnetic resonance (1H NMR) spectra of intact human urine. The presence of many of ... |
|
|
1,5-anhydroglucitol and postprandial hyperglycemia as measured by continuous glucose monitoring system in moderately controlled patients with diabetes.
Diabetes Care 29(6) , 1214-9, (2006) Postprandial hyperglycemia is often inadequately assessed in diabetes management. Serum 1,5-anhydroglucitol (1,5-AG) drops as serum glucose rises above the renal threshold for glucose and has been proposed as a marker for postprandial hyperglycemia. The objec... |
|
|
Can serum beta-hydroxybutyrate be used to diagnose diabetic ketoacidosis?
Diabetes Care 31(4) , 643-7, (2008) Current criteria for the diagnosis of diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) are limited by their nonspecificity (serum bicarbonate [HCO(3)] and pH) and qualitative nature (the presence of ketonemia/ketonuria). The present study was undertaken to determine whether quant... |
|
|
Serum 8-hydroxy-guanine levels are increased in diabetic patients.
Diabetes Care 24(4) , 733-7, (2001) The production of reactive oxygen species is increased in diabetic patients, especially in those will poor glycemic control. We have investigated oxidative damage in type 2 diabetic patients using serum 8-hydroxyguanine (8-OHG) as a biomarker.We studied 41 ty... |
|
|
D-chiro-inositol metabolism in diabetes mellitus.
Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 90(21) , 9988-92, (1993) D-chiro-inositol is a rare inositol isomer present in inositol phosphoglycans which are proposed mediators of insulin action. To study D-chiro-inositol metabolism in diabetes mellitus, a sensitive and specific assay was developed using negative-ion chemical i... |
|
|
Serum hyaluronan concentration as a marker of angiopathy in patients with diabetes mellitus.
Endocr. J. 53(6) , 761-6, (2006) Accumulation of hyaluronan (HA) around smooth muscle cells in lesions of atherosclerosis in diabetic patients suggests that this protein plays an important role in diabetic angiopathy. The aim of this study was to determine the correlation between serum HA co... |
|
|
Metabolic effects of an enteral nutrition formula for diabetes: comparison with standard formulas in patients with type 1 diabetes.
Clin. Nutr. 22(5) , 483-7, (2003) To evaluate the metabolic response (glucose, cholesterol, triglycerides and beta-hydroxy-butyrate) in patients with type 1 diabetes after a trial breakfast with an enteral nutrition formula designed for patients with diabetes and compare it with standard form... |
|
|
Comparison of oral insulin spray and subcutaneous regular insulin at mealtime in type 1 diabetes.
Diabetes Technol. Ther. 9(4) , 372-6, (2007) The aim of this study was to compare the glucose pharmacodynamics after oral spray insulin (Oral-lyn , Generex Biotechnology, Toronto, ON, Canada) and subcutaneous (sc) injection of regular insulin in 10 subjects with type 1 diabetes mellitus (T1DM).Basal the... |
|
|
Uric acid concentration in subjects at risk of type 2 diabetes mellitus: relationship to components of the metabolic syndrome.
Metab. Clin. Exp. 51(3) , 372-5, (2002) High uric acid concentration is a common finding in subjects with risk factors for cardiovascular disease (CVD), including some characteristics of the metabolic syndrome. However, its exact role in this setting and in the progression to type 2 diabetes mellit... |