纤维五糖
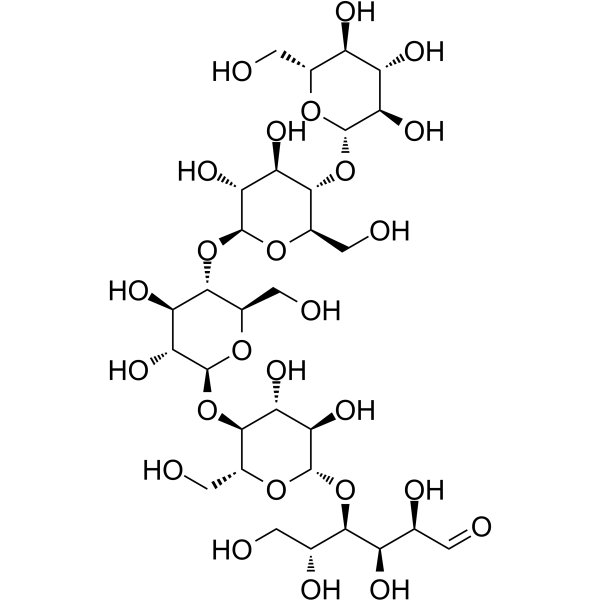
纤维五糖结构式

|
常用名 | 纤维五糖 | 英文名 | Cellopentaose |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS号 | 2240-27-9 | 分子量 | 828.718 | |
| 密度 | 1.8±0.1 g/cm3 | 沸点 | 1253.2±65.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| 分子式 | C30H52O26 | 熔点 | 245-268ºC | |
| MSDS | 中文版 美版 | 闪点 | 385.5±27.8 °C |
|
Capillary electrophoresis fingerprinting of 8-aminopyrene-1,3,6-trisulfonate derivatized nitrocellulose after partial acid depolymerization.
J. Chromatogr. A. 1387 , 134-43, (2015) Fine characterization of nitrocellulose (NC) remains a challenge, especially in forensic analysis, and a strategy consisting in obtaining representative fingerprints by a separation technique, as for proteins, is of prime interest. In this work, we first esta... |
|
|
Combining free and aggregated cellulolytic systems in the cellulosome-producing bacterium Ruminiclostridium cellulolyticum.
Biotechnol. Biofuels 8 , 114, (2015) Ruminiclostridium cellulolyticum and Lachnoclostridium phytofermentans (formerly known as Clostridium cellulolyticum and Clostridium phytofermentans, respectively) are anaerobic bacteria that developed different strategies to depolymerize the cellulose and th... |
|
|
Multifunctional cellulolytic auxiliary activity protein HcAA10-2 from Hahella chejuensis enhances enzymatic hydrolysis of crystalline cellulose.
Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 99(7) , 3041-55, (2015) The modular auxiliary activity (AA) family of proteins is believed to cause amorphogenesis in addition to oxidative cleavage of crystalline cellulose although the supporting evidence is limited. HcAA10-2 is a modular AA10 family protein (58 kDa) composed of a... |
|
|
Interaction of bacteriophage lambda with its cell surface receptor: an in vitro study of binding of the viral tail protein gpJ to LamB (Maltoporin).
Biochemistry 45(8) , 2708-20, (2006) The cell surface receptor for bacteriophage Lambda is LamB (maltoporin). Responsible for phage binding to LamB is the C-terminal part, gpJ, of phage tail protein J. To study the interaction between LamB and gpJ, a chimera protein composed of maltose binding p... |
|
|
Competitive and product inhibition-based alpha-amylase activity analysis method.
Clin. Biochem. 41(4-5) , 325-30, (2008) To propose a methodology for analyzing salivary alpha-amylase activity (sAMY) for a hand-held device that can be used easily and quickly for evaluating human psychological effects.An improved method for the analysis of sAMY is proposed using competitive and p... |
|
|
Expression and purification of cellulase Xf818 from Xylella fastidiosa in Escherichia coli.
Curr. Microbiol. 53(3) , 198-203, (2006) Xylella fastidiosa was the first plant pathogen whose complete genome sequence was available. X. fastidiosa causes citrus variegated chlorosis, but the physiological basis of the disease in unknown. Through comparative sequence analysis, several putative plan... |
|
|
Cellulase production from Pseudoalteromonas sp. NO3 isolated from the sea squirt Halocynthia rorentzi.
J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 36(11) , 1375-82, (2009) Pseudoalteromonas sp. NO3 was isolated from the hemolymph of diseased sea squirts (Halocynthia rorentzi) with symptoms of soft tunic syndrome. The strain was found to produce an extracellular cellulase (CelY) that consisted of a 1,476 bp open reading frame en... |
|
|
Application of the statistical test of equivalent pathways (STEP) method to the triple quadrupole mass spectrometer.
Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 21(20) , 3365-72, (2007) Recently, we demonstrated a new method, STEP (Statistical Test of Equivalent Pathways) analysis, which differentiates first-generation product ions (primary product ions) from second-generation product ions (secondary product ions) obtained in tandem mass spe... |
|
|
Crystal structure of the rice branching enzyme I (BEI) in complex with maltopentaose.
Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 424(3) , 508-11, (2012) Starch branching enzyme (SBE) catalyzes the cleavage of α-1,4-linkages and the subsequent transfer of α-1,4 glucan to form an α-1,6 branch point in amylopectin. We determined the crystal structure of the rice branching enzyme I (BEI) in complex with maltopent... |
|
|
Screening and characterization of a cellulase gene from the gut microflora of abalone using metagenomic library.
J. Microbiol. 49(1) , 141-5, (2011) A metagenomic fosmid library was constructed using genomic DNA isolated from abalone intestine. Screening of a library of 3,840 clones revealed a 36 kb insert of a cellulase positive clone (pAMHElO). A shotgun clone library was constructed using the positive ... |