五聚赖氨酸
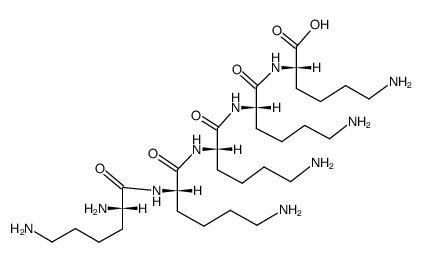
五聚赖氨酸结构式

|
常用名 | 五聚赖氨酸 | 英文名 | H-Lys-Lys-Lys-Lys-Lys-OH acetate salt |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS号 | 19431-21-1 | 分子量 | 658.87700 | |
| 密度 | N/A | 沸点 | N/A | |
| 分子式 | C30H62N10O6 | 熔点 | N/A | |
| MSDS | 中文版 美版 | 闪点 | N/A |
|
Efficacy and mechanism of action of volasertib, a potent and selective inhibitor of Polo-like kinases, in preclinical models of acute myeloid leukemia.
J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 352(3) , 579-89, (2015) Polo-like kinase 1 (Plk1), a member of the Polo-like kinase family of serine/threonine kinases, is a key regulator of multiple steps in mitosis. Here we report on the pharmacological profile of volasertib, a potent and selective Plk inhibitor, in multiple pre... |
|
|
Early life stress in fathers improves behavioural flexibility in their offspring.
Nat. Commun. 5 , 5466, (2014) Traumatic experiences in childhood can alter behavioural responses and increase the risk for psychopathologies across life, not only in the exposed individuals but also in their progeny. In some conditions, such experiences can however be beneficial and facil... |
|
|
Activation of pyruvate dehydrogenase by dichloroacetate has the potential to induce epigenetic remodeling in the heart.
J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 82 , 116-24, (2015) Dichloroacetate (DCA) promotes pyruvate entry into the Krebs cycle by inhibiting pyruvate dehydrogenase (PDH) kinase and thereby maintaining PDH in the active dephosphorylated state. DCA has recently gained attention as a potential metabolic-targeting therapy... |
|
|
Epigenetics and miRNA as predictive markers and targets for lung cancer chemotherapy.
Cancer Biol. Ther. 16 , 1056-70, (2015) Lung cancer cells show inherent and acquired resistance to chemotherapy. The lack of good predictive markers/novel targets and the incomplete understanding of the mechanisms of resistance limit the success of lung cancer response to chemotherapy. In the prese... |
|
|
Evaluation of azacitidine and entinostat as sensitization agents to cytotoxic chemotherapy in preclinical models of non-small cell lung cancer.
Oncotarget 6(1) , 56-70, (2015) Recent clinical data in lung cancer suggests that epigenetically targeted therapy may selectively enhance chemotherapeutic sensitivity. There have been few if any studies rigorously evaluating this hypothesized priming effect. Here we describe a series of inv... |
|
|
Histone Deacetylase Inhibitors Antagonize Distinct Pathways to Suppress Tumorigenesis of Embryonal Rhabdomyosarcoma.
PLoS ONE 10 , e0144320, (2015) Embryonal rhabdomyosarcoma (ERMS) is the most common soft tissue cancer in children. The prognosis of patients with relapsed or metastatic disease remains poor. ERMS genomes show few recurrent mutations, suggesting that other molecular mechanisms such as epig... |
|
|
Histone acetylation mediated by Brd1 is crucial for Cd8 gene activation during early thymocyte development.
Nat. Commun. 5 , 5872, (2014) During T-cell development, Cd8 expression is controlled via dynamic regulation of its cis-regulatory enhancer elements. Insufficiency of enhancer activity causes variegated Cd8 expression in CD4(+)CD8(+) double-positive (DP) thymocytes. Brd1 is a subunit of t... |
|
|
Double-shell gold nanoparticle-based DNA-carriers with poly-L-lysine binding surface.
Biomaterials 32 , 3312-3321, (2011) In view of the prospective applications of polyamine coatings in functional gold nanoparticles for use as carriers in gene delivery systems, in tissue repair and as bactericidal and virucidal non-toxic vehicle, we have investigated the interactions of poly-l-... |
|
|
Mechanistic differences in DNA nanoparticle formation in the presence of oligolysines and poly-L-lysine.
Biomacromolecules 8 , 477-484, (2007) We studied the effectiveness of trilysine (Lys3), tetralysine (Lys4), pentalysine (Lys5), and poly-l-lysine (PLL) (MW 50000) on lambda-DNA nanoparticle formation and characterized the size, shape, and stability of nanoparticles. Light scattering experiments s... |
|
|
Effect of association with sulfate on the electrophoretic mobility of polyarginine and polylysine.
J. Phys. Chem. B 114 , 11934-11941, (2010) Domains rich in cationic amino acids are ubiquitous in peptides with the ability to cross cell membranes, which is likely related to the binding of such polypeptides to anionic groups on the membrane surface. To shed more light on these interactions, we inves... |