特立氟胺
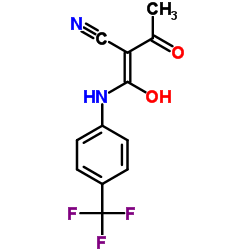
特立氟胺结构式

|
常用名 | 特立氟胺 | 英文名 | teriflunomide |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS号 | 108605-62-5 | 分子量 | 270.207 | |
| 密度 | 1.4±0.1 g/cm3 | 沸点 | 363.0±42.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| 分子式 | C12H9F3N2O2 | 熔点 | N/A | |
| MSDS | 美版 | 闪点 | 173.3±27.9 °C | |
| 符号 |

GHS07 |
信号词 | Warning |
特立氟胺用途(E/Z)-Teriflunomide((E/Z)-A77 1726)是来氟米特(HY-B0083)的活性代谢物。来氟米特是一种免疫调节剂,可通过抑制线粒体酶二氢乳清酸脱氢酶(DHODH)发挥作用。来氟米特可用于类风湿性关节炎(RA)的研究[1]。 |
| 中文名 | 2-氰基-3-羟基-N-[4-(三氟甲基)苯基]-2-丁烯酰胺 |
|---|---|
| 英文名 | 2-Cyano-3-hydroxy-N-(4-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl)but-2-enamide,teriflunomide |
| 中文别名 | 特立氟胺 |
| 英文别名 | 更多 |
| 密度 | 1.4±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| 沸点 | 363.0±42.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| 分子式 | C12H9F3N2O2 |
| 分子量 | 270.207 |
| 闪点 | 173.3±27.9 °C |
| 精确质量 | 270.061615 |
| PSA | 73.12000 |
| LogP | 0.71 |
| 外观性状 | 白色固体 |
| 蒸汽压 | 0.0±0.9 mmHg at 25°C |
| 折射率 | 1.552 |
| 储存条件 | +2C to +8C |
| 分子结构 | 1、摩尔折射率:60.59 2、摩尔体积(cm3/mol):189.6 3、等张比容(90.2K):492.1 4、表面张力(dyne/cm):45.3 5、介电常数:无可用的 6、极化率(10-24cm3):24.02 7、单一同位素质量:270.061612 Da 8、标称质量:270 Da 9、平均质量:270.2073 Da |
| 计算化学 | 1.疏水参数计算参考值(XlogP):3.3 2.氢键供体数量:2 3.氢键受体数量:6 4.可旋转化学键数量:2 5.互变异构体数量:8 6.拓扑分子极性表面积73.1 7.重原子数量:19 8.表面电荷:0 9.复杂度:426 10.同位素原子数量:0 11.确定原子立构中心数量:0 12.不确定原子立构中心数量:0 13.确定化学键立构中心数量:1 14.不确定化学键立构中心数量:0 15.共价键单元数量:1 |
|
Hepatic cytochrome P450s attenuate the cytotoxicity induced by leflunomide and its active metabolite A77 1726 in primary cultured rat hepatocytes.
Toxicol. Sci. 122(2) , 579-86, (2011) The Black Box Warning section of the U.S. drug label for leflunomide was recently updated to include stronger warnings about potential hepatotoxicity from this novel anti-arthritis drug. Because metab... |
|
|
Respiratory syncytial virus inhibits lung epithelial Na+ channels by up-regulating inducible nitric-oxide synthase.
J. Biol. Chem. 284(11) , 7294-306, (2009) Respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) infection has been shown to reduce Na+-driven alveolar fluid clearance in BALB/c mice in vivo. To investigate the cellular mechanisms by which RSV inhibits amiloride-... |
|
|
Induction of EMT-like phenotypes by an active metabolite of leflunomide and its contribution to pulmonary fibrosis.
Cell Death Differ. 17(12) , 1882-95, (2010) Drug-induced interstitial lung disease (ILD), particularly pulmonary fibrosis, is a serious clinical concern and myofibroblasts have been suggested to have a major role, with it recently being reveale... |
| 2-Butenamide (2-cyano-3-hydroxy-N-[4-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl] |
| Butanenitrile, 2-[hydroxy[[4-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]amino]methylene]-3-oxo-, (2Z)- |
| (2Z)-2-(Hydroxy{[4-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]amino}methylene)-3-oxobutanenitrile |
| 2-Cyano-3-hydroxy-N-(4-trifluoromethylphenyl)crotonamide |
| Teriflunomide |
| 2-Cyano-3-hydroxy-N-(4-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl)but-2-enamide |


