羟乙基脱乙酰壳多糖
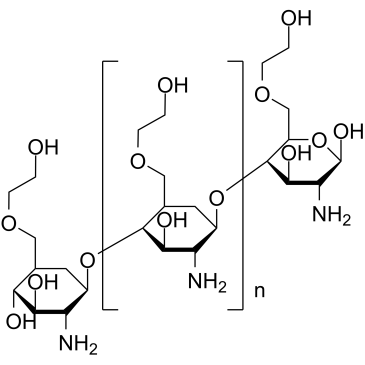
羟乙基脱乙酰壳多糖结构式

|
常用名 | 羟乙基脱乙酰壳多糖 | 英文名 | GLYCOL CHITOSAN |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS号 | 123938-86-3 | 分子量 | N/A | |
| 密度 | N/A | 沸点 | N/A | |
| 分子式 | N/A | 熔点 | N/A | |
| MSDS | 美版 | 闪点 | N/A |
羟乙基脱乙酰壳多糖用途Glycol chitosan 是一种具有亲水性乙二醇支链的壳聚糖衍生物。Glycol chitosan 增强了Glycine max Harosoy 63W 细胞的膜通透性和渗漏。Glycol chitosan 是水溶性的,生物相容性和可生物降解的。Glycol chitosan 可抑制大肠杆菌,金黄色葡萄球菌和肠炎链球菌的生长,MIC 值分别为 4 μg/mL,32 μg/m L和 <0.5 μg/mL。 |
| 中文名 | 羟乙基脱乙酰壳多糖 |
|---|---|
| 英文名 | GLYCOL CHITOSAN |
| 英文别名 | 更多 |
| 描述 | Glycol chitosan 是一种具有亲水性乙二醇支链的壳聚糖衍生物。Glycol chitosan 增强了Glycine max Harosoy 63W 细胞的膜通透性和渗漏。Glycol chitosan 是水溶性的,生物相容性和可生物降解的。Glycol chitosan 可抑制大肠杆菌,金黄色葡萄球菌和肠炎链球菌的生长,MIC 值分别为 4 μg/mL,32 μg/m L和 <0.5 μg/mL。 |
|---|---|
| 相关类别 | |
| 靶点 |
MIC: 4 μg/mL (E. coli), 32 μg/mL (S. aureus) and <0.5 μg/mL (S. enteritidis)[4] |
| 体外研究 | 乙二醇壳聚糖衍生物已成功地应用于药物、基因、光敏剂等抗菌药物和抗癌药物的物理包封或化学偶联。乙二醇壳聚糖可以直接与疏水性药物连接,生成两亲性化合物,也可以形成纳米颗粒(NPs)用于细胞成像和药物传递。将乙二醇壳聚糖衍生物用于细胞成像和药物传递具有许多优点,包括基于增强的渗透性和保留(EPR)效应的乙二醇壳聚糖NPs具有极好的肿瘤归巢能力、低细胞毒性、易于化学改性、高生物相容性和可生物降解性[1]。乙二醇壳聚糖的疏水改性已经得到证实,如含5β-胆酸部分的乙二醇壳聚糖和脱氧胆酸乙二醇壳聚糖,可以自组装成纳米粒子,作为疏水药物和基因的载体[2]。 |
| 参考文献 |
| InChIKey | BMSOSHUYFHAULE-GBSNKSGZSA-N |
|---|---|
| SMILES | N.NC1C(OC2C(COCCO)CC(OC3C(COCCO)OC(O)C(N)C3O)C(N)C2O)CC(COCCO)C(O)C1O |
| 外观性状 | crystalline |
| 储存条件 | −20°C |
| 个人防护装备 | Eyeshields;Gloves;type N95 (US);type P1 (EN143) respirator filter |
|---|---|
| 危害码 (欧洲) | Xi |
| 危险品运输编码 | NONH for all modes of transport |
| WGK德国 | 3 |
|
Effect of Chitosan on Membrane Permeability of Suspension-Cultured Glycine max and Phaseolus vulgaris Cells.
Plant Physiol. 70 , 1449-1454, (1982) Treatment of suspension-cultured Glycine max cv Harosoy 63 cells with soluble chitosan (20-500 micrograms per milliliter) increased membrane permeability as shown by leakage of electrolytes, protein, ... |
|
|
Pilot in vivo toxicological investigation of boron nitride nanotubes.
Int. J. Nanomedicine 7 , 19-24, (2012) Boron nitride nanotubes (BNNTs) have attracted huge attention in many different research fields thanks to their outstanding chemical and physical properties. During recent years, our group has pioneer... |
|
|
Barium Titanate Nanoparticles: Highly Cytocompatible Dispersions in Glycol-chitosan and Doxorubicin Complexes for Cancer Therapy.
Nanoscale Res. Lett. 5 , 1093-101, (2011) In the latest years, innovative nanomaterials have attracted a dramatic and exponentially increasing interest, in particular for their potential applications in the biomedical field. In this paper, we... |
| MFCD00131218 |


