辛酸
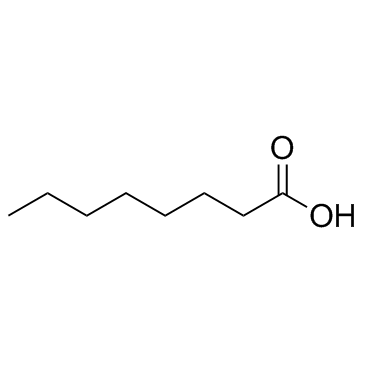
辛酸结构式

|
常用名 | 辛酸 | 英文名 | Octanoic acid |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS号 | 124-07-2 | 分子量 | 144.21100 | |
| 密度 | 0.91 g/mL at 25 °C(lit.) | 沸点 | 237 ºC | |
| 分子式 | C8H16O2 | 熔点 | 16 °C | |
| MSDS | 中文版 美版 | 闪点 | 130 ºC | |
| 符号 |

GHS05 |
信号词 | Danger |
辛酸用途Octanoic acid 是一种油性液体,带有些许腐臭味,能用于酯类香料和染料的生产。 |
| 中文名 | 正辛酸 |
|---|---|
| 英文名 | octanoic acid |
| 中文别名 | 辛癸混合酸 | 辛酸 | 辛酸,羊脂酸,C8酸 | 羊脂酸 |
| 英文别名 | 更多 |
| 密度 | 0.91 g/mL at 25 °C(lit.) |
|---|---|
| 沸点 | 237 ºC |
| 熔点 | 16 °C |
| 分子式 | C8H16O2 |
| 分子量 | 144.21100 |
| 闪点 | 130 ºC |
| 精确质量 | 144.11500 |
| PSA | 37.30000 |
| LogP | 2.43150 |
| InChIKey | WWZKQHOCKIZLMA-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| SMILES | CCCCCCCC(=O)O |
| 外观性状 | 淡黄色特有的液体 |
| 蒸汽密度 | 5 (vs air) |
| 蒸汽压 | 0.022mmHg at 25°C |
| 折射率 | n20/D 1.428(lit.) |
| 储存条件 | 应放在远离火源的阴凉通风处。 |
| 稳定性 | 1.基本性质:以酯的形式存在于椰子油、柠檬叶油和羊毛脂中。以游离态存在于西藏柏木(Cupressus tolurosa)、日本柳杉(Cryptomeria japonica)、烟草、肉豆蔻等植物精油中。 2. 存在于烤烟烟叶、白肋烟烟叶、香料烟烟叶、主流烟气中。 3. 天然存在于苹果、小麦面包中。 |
| 水溶解性 | 0.68 g/L (20 ºC) |
| 分子结构 | 1、 摩尔折射率:40.67 2、 摩尔体积(cm3/mol):155.2 3、 等张比容(90.2K):372.2 4、 表面张力(dyne/cm):33.0 5、 极化率(10-24cm3):16.12 |
| 计算化学 | 1.疏水参数计算参考值(XlogP):无 2.氢键供体数量:1 3.氢键受体数量:2 4.可旋转化学键数量:6 5.互变异构体数量:无 6.拓扑分子极性表面积37.3 7.重原子数量:10 8.表面电荷:0 9.复杂度:89.3 10.同位素原子数量:0 11.确定原子立构中心数量:0 12.不确定原子立构中心数量:0 13.确定化学键立构中心数量:0 14.不确定化学键立构中心数量:0 15.共价键单元数量:1 |
| 更多 | 1. 性状:有汗臭味的无色透明状液体。 2. 沸点(ºC,101.3kPa):239.7 3. 熔点(ºC):16.5 4. 相对密度(g/mL,20/4ºC):0.9073 5. 相对密度(g/mL,25/4ºC):0.9066 6. 相对蒸汽密度(g/mL,空气=1):5 7. 折射率(n20ºC):1.4280 8. 折射率(n25ºC):1.4261 9. 黏度(mPa·s,20ºC):5.828 10. 黏度(mPa·s,30ºC):4.690 11. 闪点(ºC):>110 12. 蒸发热(KJ/mol,134ºC):70.05 13. 蒸发热(KJ/mol,b.p.):58.49 14. 熔化热(KJ/mol):21.39 15. 比热容(KJ/(kg·K),16~36ºC,定压):2.15 16. 电导率(S/m,80ºC):3.7×10-3 17. 蒸气压(kPa,92ºC):0.13 18. 离解常数(25ºC,水中):1.27×10-5 19. 溶解性:能溶于醚、氯仿、二硫化碳、石油醚和冰乙酸、乙酸乙酯等有机溶剂。20℃时在100g水中溶解0.068g,60℃时溶解0.113g。14.4℃时水在辛酸中溶解3.88%。10℃时在100g苯中溶770g。0℃时在100g乙醇中溶解262g,10℃时溶解1035g。0℃时在100g异丙醇中溶解280g,10℃时溶解990g。 20. 临界温度(ºC):419.85 21. 临界压力(MPa):2.87 22. 临界密度(g·cm-3):0.278 23. 临界体积(cm3·mol-1):519 24. 临界压缩因子:0.259 25. 偏心因子:0.779 26. 溶度参数(J·cm-3)0.5:22.324 27. van der Waals面积(cm2·mol-1):1.328×1010 28. van der Waals体积(cm3·mol-1):94.790 29. 气相标准燃烧热(焓)(kJ·mol-1):-4880.4 30. 气相标准声称热(焓)( kJ·mol-1) :-554.2 31. 液相标准燃烧热(焓)(kJ·mol-1):-4798.7 32. 液相标准声称热(焓)( kJ·mol-1):-636.0 33. 液相标准热熔(J·mol-1·K-1):332.4 |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
辛酸毒理学数据: 1、皮肤/眼睛刺激:兔子眼睛标准德雷兹染眼实验:500mg/24H 对眼睛有中等强度的刺激作用 2、急性毒性:大鼠经口LD50:10080mg/kg;小鼠经静脉注射LC50:600mg/kg 兔子皮肤LD50:>5gm/kg 3、致突变:酿酒酵母性染色体亏损和不分离测试系统:5ppm |
| 符号 |

GHS05 |
|---|---|
| 信号词 | Danger |
| 危害声明 | H314 |
| 警示性声明 | P280-P303 + P361 + P353-P304 + P340 + P310-P305 + P351 + P338 |
| 个人防护装备 | Faceshields;full-face respirator (US);Gloves;Goggles;multi-purpose combination respirator cartridge (US);type ABEK (EN14387) respirator filter |
| 危害码 (欧洲) | C:Corrosive |
| 风险声明 (欧洲) | R34 |
| 安全声明 (欧洲) | S26-S36/39-S45-S36/37/39-S25 |
| 危险品运输编码 | UN 3265 8/PG 3 |
| WGK德国 | 1 |
| RTECS号 | RH0175000 |
| 包装等级 | III |
| 危险类别 | 8 |
| 海关编码 | 2915900090 |
| 辛酸上游产品 10 | |
|---|---|
| 辛酸下游产品 10 | |
生产方法简述:工业上生产辛酸是采用辛醛为原料,在实验室制备时采用正己基丙二酸加热放出二氧化碳,减压至4-6.65kPa使反应完全。最后将反应产物减压蒸馏,收集127-129℃(2.13kPa)馏分即为辛酸。收率80-85%。由1-辛烯和过醋酸反应可制得辛酸。此外还有正辛醇氧化脱氢法。
精制方法:用分子筛脱水后减压分馏。也可用分步结晶法精制。
1.辛醛氧化法
2.正己基丙二酸法
3.正辛醇氧化脱氢法
4.1-辛烯法 由1-辛烯和过醋酸反应制得:
5.烟草:OR,44;OR,49;BU,56;OR,26;FC,9, 18;BU,18;OR,18;BU,26;FC,40。合成:由椰子油皂化后再酸化合分馏而得。
| 海关编码 | 2915900090 |
|---|---|
| 中文概述 | 2915900090. 其他饱和无环一元羧酸及其酸酐(酰卤、过氧)化物、过氧酸及其卤化、硝化、磺化、亚硝化衍生物. 增值税率:17.0%. 退税率:9.0%. 监管条件:AB(入境货物通关单,出境货物通关单). 最惠国关税:5.5%. 普通关税:30.0% |
| 申报要素 | 品名, 成分含量, 用途 |
| 监管条件 | A.入境货物通关单 B.出境货物通关单 |
| 检验检疫 | R.进口食品卫生监督检验 S.出口食品卫生监督检验 M.进口商品检验 N.出口商品检验 |
| Summary | 2915900090 other saturated acyclic monocarboxylic acids and their anhydrides, halides, peroxides and peroxyacids; their halogenated, sulphonated, nitrated or nitrosated derivatives VAT:17.0% Tax rebate rate:9.0% Supervision conditions:AB(certificate of inspection for goods inward,certificate of inspection for goods outward) MFN tariff:5.5% General tariff:30.0% |
|
Sensing of triacylglycerol in the gut: different mechanisms for fatty acids and 2-monoacylglycerol.
J. Physiol. 593(8) , 2097-109, (2015) Sensing of dietary triacylglycerol in the proximal small intestine results in physiological, hormonal and behavioural responses. However, the exact physiological pathways linking intestinal fat sensin... |
|
|
Combined effects of nutrients and temperature on the production of fermentative aromas by Saccharomyces cerevisiae during wine fermentation.
Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 99(5) , 2291-304, (2015) Volatile compounds produced by yeast during fermentation greatly influence the organoleptic qualities of wine. We developed a model to predict the combined effects of initial nitrogen and phytosterol ... |
|
|
Olfactometry Profiles and Quantitation of Volatile Sulfur Compounds of Swiss Tilsit Cheeses.
J. Agric. Food Chem. 63 , 7511-21, (2015) To establish the odor profiles of three differently fabricated commercial Swiss Tilsit cheeses, analyses were conducted using headspace solid-phase microextraction gas chromatography-mass spectrometry... |
| Octylic acid |
| n-Octoic acid |
| OCTANOIC ACID/CAPRYLIC ACID |
| n-Octanoic Acid |
| MFCD00004429 |
| Octocapric Acid |
| Acid C8,Caprylic acid |
| CAPRYLIC ACID (C8) |
| OCTANOIC ACID (CAPRYLIC) |
| heptane-7-carboxylic acid |
| Octanoic acid |
| caprylic acid |
| n-octylic acid |
| n-caprylic acid |
| octoic acid |
| OCTANOICACID |
| NATURAL CAPRYLIC ACID FEMA NO.2799 |
| 1-HEPTANECARBOXYLIC ACID |
| CAPRYLICACID |
| neo-fat 8 |
| OCTANOIC ACID FOR SYNTHESIS |
| CAPRYLIC ACID NATURAL |
| EINECS 204-677-5 |

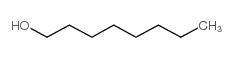 CAS号111-87-5
CAS号111-87-5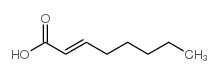 CAS号1871-67-6
CAS号1871-67-6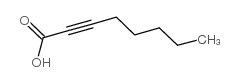 CAS号5663-96-7
CAS号5663-96-7 CAS号124-13-0
CAS号124-13-0 CAS号201230-82-2
CAS号201230-82-2 CAS号124-11-8
CAS号124-11-8 CAS号818-44-0
CAS号818-44-0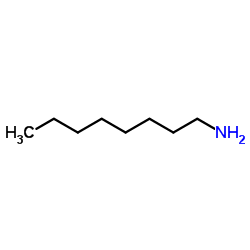 CAS号111-86-4
CAS号111-86-4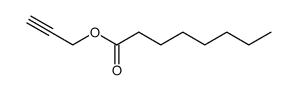 CAS号2638-36-0
CAS号2638-36-0 CAS号111-66-0
CAS号111-66-0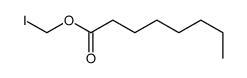 CAS号111013-41-3
CAS号111013-41-3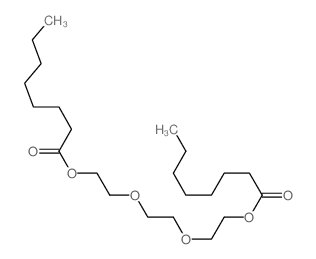 CAS号106-10-5
CAS号106-10-5 CAS号376-27-2
CAS号376-27-2 CAS号593-39-5
CAS号593-39-5 CAS号423-54-1
CAS号423-54-1 CAS号59558-23-5
CAS号59558-23-5 CAS号36946-07-3
CAS号36946-07-3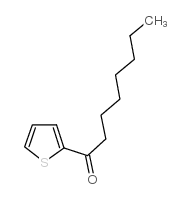 CAS号30711-41-2
CAS号30711-41-2 CAS号538-23-8
CAS号538-23-8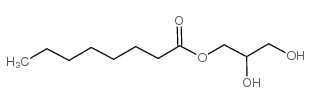 CAS号19670-49-6
CAS号19670-49-6






