Ureidopropionic acid
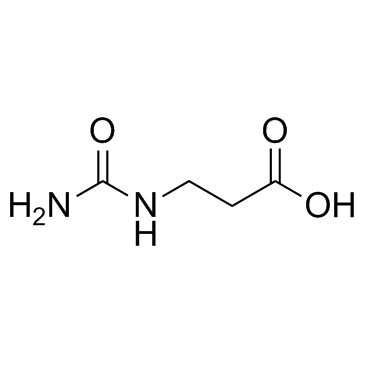
Ureidopropionic acid structure
|
Common Name | Ureidopropionic acid | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 462-88-4 | Molecular Weight | 132.11800 | |
| Density | 1.337g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 324.8ºC at 760mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C4H8N2O3 | Melting Point | 170-175ºC (dec.) | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 150.2ºC | |
|
Improved colorimetric procedure for quantitating N-carbamoyl-beta-alanine with minimum dihydrouracil interference.
Anal. Biochem. 122(2) , 345-7, (1982)
|
|
|
Sensitive method for the quantification of urinary pyrimidine metabolites in healthy adults by gas chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry.
J. Chromatogr. B. Analyt. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 791(1-2) , 371-80, (2003) Enzyme deficiencies in pyrimidine metabolism are associated with a risk for severe toxicity against the antineoplastic agent 5-fluorouracil. To assess whether urinary levels of pyrimidines and their metabolites can be used for predicting patients' individual ... |
|
|
Comprehensive analysis of pyrimidine metabolism in 450 children with unspecific neurological symptoms using high-pressure liquid chromatography-electrospray ionization tandem mass spectrometry.
J. Inherit. Metab. Dis. 28(6) , 1109-22, (2005) To evaluate the significance of inborn metabolic disorders of the pyrimidine degradation pathway, 450 children with unspecific neurological symptoms were comprehensively studied; 200 healthy children were recruited as controls. Uracil and thymine as well as t... |
|
|
3-Ureidopropionate contributes to the neuropathology of 3-ureidopropionase deficiency and severe propionic aciduria: a hypothesis.
J. Neurosci. Res. 66(4) , 666-73, (2001) 3-Ureidopropionate (3-UPA) is a physiologic metabolite in pyrimidine degradation. Pathological accumulation of 3-UPA in body fluids is found in 3-ureidopropionase deficiency and severe forms of propionic aciduria. Both diseases clinically present with a sever... |
|
|
Assay for beta-ureidopropionase by high-performance liquid chromatography.
Anal. Biochem. 188(1) , 233-6, (1990) A sensitive assay for beta-ureidopropionase based on derivatization of the reaction product beta-alanine with phenylisothiocyanate has been developed. Purification of the resulting phenylthiocarbamoyl-beta-alanine is achieved on a LiChrospher 100 C18 reversed... |
|
|
Simple method for the quantitative analysis of dihydropyrimidines and N-carbamyl-beta-amino acids in urine.
Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 309B , 15-9, (1991)
|
|
|
beta-Ureidopropionase deficiency: a novel inborn error of metabolism discovered using NMR spectroscopy on urine.
Magn. Reson. Med. 46(5) , 1014-7, (2001) In this work, NMR investigations that led to the discovery of a new inborn error of metabolism, beta-ureidopropionase (UP) deficiency, are reported. 1D (1)H-NMR experiments were performed using a patient's urine. 3-Ureidopropionic acid was observed in elevate... |
|
|
Liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometric assay for the analysis of uracil, 5,6-dihydrouracil and beta-ureidopropionic acid in urine for the measurement of the activities of the pyrimidine catabolic enzymes.
J. Chromatogr. B. Analyt. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 839(1-2) , 45-53, (2006) A liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometric assay for the determination of uracil, 5,6-dihydrouracil and beta-ureidopropionic acid in urine was developed to measure the activities of enzymes involved in pyrimidine breakdown. The assay was required to in... |
|
|
Enzymes of uracil catabolism in normal and neoplastic human tissues.
Cancer Res. 45(11 Pt 1) , 5405-12, (1985) Enzymes of the pyrimidine base catabolism, dihydrouracil dehydrogenase (EC 1.3.1.2), dihydropyrimidinase (EC 3.5.2.2), and beta-ureidopropionase (EC 3.5.1.6) were compared in the cytosolic extract of several normal and neoplastic human tissues. The activity w... |
|
|
Clinical, biochemical and genetic findings in two siblings with a dihydropyrimidinase deficiency.
Mol. Genet. Metab. 91(2) , 157-64, (2007) Dihydropyrimidinase (DHP) is the second enzyme of the pyrimidine degradation pathway and it catalyses the ring opening of 5,6-dihydrouracil and 5,6-dihydrothymine to N-carbamyl-beta-alanine and N-carbamyl-beta-aminoisobutyric acid, respectively. To date, only... |