tilmicosin
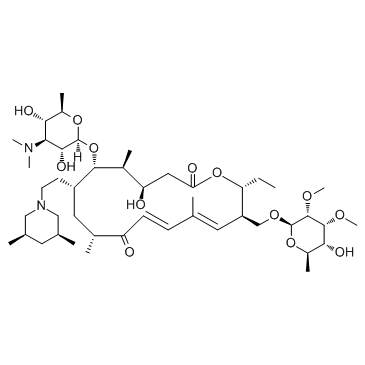
tilmicosin structure
|
Common Name | tilmicosin | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 108050-54-0 | Molecular Weight | 869.133 | |
| Density | 1.2±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 926.6±65.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C46H80N2O13 | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | Chinese | Flash Point | 514.2±34.3 °C | |
|
Extraction of trace tilmicosin in real water samples using ionic liquid-based aqueous two-phase systems.
Water Sci. Technol. 67(8) , 1671-7, (2013) The effective method of ionic liquid-based aqueous two-phase extraction, which involves ionic liquid (IL) (1-butyl-3-methyllimidazolium chloride, [C4mim]Cl) and inorganic salt (K2HPO4) coupled with high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC), has been used ... |
|
|
Antimicrobial susceptibility of Actinobacillus pleuropneumoniae isolates from clinical outbreaks of porcine respiratory diseases.
Vet. Microbiol. 150(1-2) , 203-6, (2011) Limited data regarding the susceptibility of Actinobacillus pleuropneumoniae to antimicrobials has been published during recent years. Accordingly, the aim of the present study was to investigate the distribution of MICs for the isolates of A. pleuropneumonia... |
|
|
Kinetics and intrapulmonary disposition of tilmicosin after single and repeated oral bolus administrations to rabbits.
Vet. Res. Commun. 34 Suppl 1 , S69-72, (2010) Tilmicosin (TIM, Pulmotil) was administered to eight rabbits by oral gavage at a dose of 12.5 mg/kg body weight for 2, 5, and 7 days, and its plasma kinetics and intrapulmonary disposition were investigated. TIM concentrations in plasma samples collected afte... |
|
|
Generation of reduced macrolide analogs by regio-specific biotransformation.
J. Antibiot. 64(1) , 155-7, (2011)
|
|
|
Transcriptional profiling of Haemophilus parasuis SH0165 response to tilmicosin.
Microb. Drug Resist. 18(6) , 604-15, (2012) The Haemophilus parasuis respiratory tract pathogen poses a severe threat to the swine industry despite available antimicrobial therapies. To gain a more detailed understanding of the molecular mechanisms underlying H. parasuis response to tilmicosin treatmen... |
|
|
The controlled release of tilmicosin from silica nanoparticles.
Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 37(6) , 714-8, (2011) The aim of this study was to use silica nanoparticles as the carrier for controlled release of tilmicosin. Tilmicosin was selected as a drug model molecule because it has a lengthy elimination half-life and a high concentration in milk after subcutaneous admi... |
|
|
Immunosuppressive activity of tilmicosin on the immune responses in mice.
Immunopharmacol. Immunotoxicol. 33(2) , 323-8, (2011) Tilmicosin, a semi-synthetic macrolide antibiotic that is only used in the veterinary clinic, was evaluated for its immunosuppressive activity on the immune responses to ovalbumin (OVA) in mice. Tilmicosin suppressed concanavalin A (Con A)- and lipopolysaccha... |
|
|
Comparison of enrofloxacin and ceftiofur sodium for the treatment of relapse of undifferentiated fever/bovine respiratory disease in feedlot cattle.
Can. Vet. J. 53(1) , 57-62, (2012) This commercial field trial compared the efficacy of enrofloxacin and ceftiofur sodium in beef cattle at high risk of developing undifferentiated fever (UF), also known as bovine respiratory disease (BRD) that received tilmicosin at feedlot arrival, were diag... |
|
|
Anti-inflammatory effects of tilmicosin in a noninfectious mouse model of allergic asthma.
Immunopharmacol. Immunotoxicol. 33(4) , 626-32, (2011) Tilmicosin, a semi-synthetic tylosin-derived macrolide antibiotic commonly used by veterinarians, has been shown to possess anti-inflammatory activity. However, possible use in asthma treatment has not yet been studied. In this study, we investigated the anti... |
|
|
[Binding of tylosin, tilmicosin and oxytetracycline to proteins from honeybees, larvae and beehive products].
Rev. Argent. Microbiol. 42(4) , 279-83, (2010) American Foulbrood (AFB) caused by the spore-forming bacterium Paenibacillus larvae is the most serious disease of bacterial origin affecting larvae and pupae of honeybees. Antibiotics are used in many countries for the control of AFB in high incidence areas,... |