tert-Butyl acetoacetate
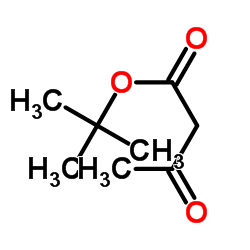
tert-Butyl acetoacetate structure
|
Common Name | tert-Butyl acetoacetate | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 1694-31-1 | Molecular Weight | 158.195 | |
| Density | 1.0±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 184.0±8.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C8H14O3 | Melting Point | -38 °C | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 60.6±0.0 °C | |
|
Itraconazole suppresses the growth of glioblastoma through induction of autophagy: involvement of abnormal cholesterol trafficking.
Autophagy 10(7) , 1241-55, (2014) Glioblastoma is one of the most aggressive human cancers with poor prognosis, and therefore a critical need exists for novel therapeutic strategies for management of glioblastoma patients. Itraconazole, a traditional antifungal drug, has been identified as a ... |
|
|
Galectin-3 contributes to luteolysis by binding to Beta 1 integrin in the bovine corpus luteum.
Biol. Reprod. 91(1) , 2, (2014) Luteolysis is characterized by a reduction in progesterone (P4) production and tissue degeneration in the corpus luteum (CL). One of major events during luteolysis is luteal cell death. Galectin-3, a ubiquitously expressed protein involved in many cellular pr... |
|
|
SUMO1 promotes Aβ production via the modulation of autophagy.
Autophagy 11(1) , 100-12, (2015) Autophagy is one of the main mechanisms in the pathophysiology of neurodegenerative disease. The accumulation of autophagic vacuoles (AVs) in affected neurons is responsible for amyloid-β (Aβ) production. Previously, we reported that SUMO1 (small ubiquitin-li... |
|
|
Inhibition of autophagy as a new means of improving chemotherapy efficiency in high-LC3B triple-negative breast cancers.
Autophagy 10(12) , 2122-42, (2015) The triple-negative breast cancer (TN BC) subtype is the most aggressive form of invasive BC. Despite intensive efforts to improve BC treatments, patients with TN BC continue to exhibit poor survival, with half developing resistance to chemotherapy. Here we i... |
|
|
Microvascular lesions by estrogen-induced ID3: its implications in cerebral and cardiorenal vascular disease.
J. Mol. Neurosci. 55(3) , 618-31, (2015) Severe symptoms of cerebral and cardiorenal vascular diseases can be triggered when cerebral, coronary, or glomerular arterioles grow inappropriately as a result of abnormal cell proliferation. The risk factor(s) and molecular mechanisms responsible for micro... |
|
|
ATG16L1 phosphorylation is oppositely regulated by CSNK2/casein kinase 2 and PPP1/protein phosphatase 1 which determines the fate of cardiomyocytes during hypoxia/reoxygenation.
Autophagy 11 , 1308-25, (2015) Recent studies have shown that the phosphorylation and dephosphorylation of ULK1 and ATG13 are related to autophagy activity. Although ATG16L1 is absolutely required for autophagy induction by affecting the formation of autophagosomes, the post-translational ... |
|
|
The PRKAA1/AMPKα1 pathway triggers autophagy during CSF1-induced human monocyte differentiation and is a potential target in CMML.
Autophagy 11 , 1114-29, (2015) Autophagy is induced during differentiation of human monocytes into macrophages that is mediated by CSF1/CSF-1/M-CSF (colony stimulating factor 1 [macrophage]). However, little is known about the molecular mechanisms that link CSF1 receptor engagement to the ... |
|
|
Gut microbes promote colonic serotonin production through an effect of short-chain fatty acids on enterochromaffin cells.
FASEB J. 29 , 1395-403, (2015) Gut microbiota alterations have been described in several diseases with altered gastrointestinal (GI) motility, and awareness is increasing regarding the role of the gut microbiome in modulating GI function. Serotonin [5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT)] is a key reg... |
|
|
Antiviral Effect of Interferon Lambda Against Lymphocytic Choriomeningitis Virus.
J. Interferon Cytokine Res. 35 , 540-53, (2015) Lambda interferons inhibit replication of many viruses, but their role in the inhibition of lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus (LCMV) infection remains unclear. In this study, we examined the antiviral effects of interferon (IFN)-λ2 and IFN-λ3 against LCMV in... |
|
|
High intralocus variability and interlocus recombination promote immunological diversity in a minimal major histocompatibility system.
BMC Evol. Biol. 14 , 273, (2015) The genes of the major histocompatibility complex (MHC/MH) have attracted considerable scientific interest due to their exceptional levels of variability and important function as part of the adaptive immune system. Despite a large number of studies on MH cla... |