Prostaglandin F1α
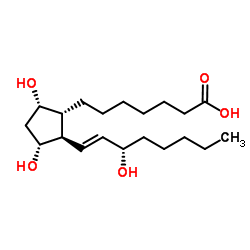
Prostaglandin F1α structure
|
Common Name | Prostaglandin F1α | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 745-62-0 | Molecular Weight | 356.497 | |
| Density | 1.1±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 526.5±50.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C20H36O5 | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 286.3±26.6 °C | |
|
Influence of human low density and high density lipoprotein cholesterol on the in vitro prostaglandin I2 synthetase activity.
Biochim. Biophys. Acta 620(3) , 352-5, (1980) We investigated in vitro the influence of low density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol and high density lioprotein (HDL) cholesterol separated from human serum on prostaglandin I2 synthetase activity studied by the conversion of prostaglandin H2 to prostaglandin... |
|
|
Native pentameric C-reactive protein displays more potent pro-atherogenic activities in human aortic endothelial cells than modified C-reactive protein.
Atherosclerosis 184(1) , 48-52, (2006) Inflammation is pivotal in atherogenesis. Numerous prospective studies have shown that levels of high sensitive C-reactive protein (CRP) predict cardiovascular events. Recently, data suggests that CRP could be a mediator in atherothrombosis. Loss of pentameri... |
|
|
Long-term fenofibrate treatment impairs endothelium-dependent dilation to acetylcholine by altering the cyclooxygenase pathway.
Cardiovasc. Res. 75(2) , 398-407, (2007) Experimental studies and opinion articles emphasize that cardiovascular alterations associated with ageing can be improved by the long-term use of fenofibrates. We analyzed the effect of fenofibrate treatment on the acetylcholine-induced relaxation in rat aor... |
|
|
The effect of the pro-inflammatory cytokine tumor necrosis factor-alpha on human joint capsule myofibroblasts.
Arthritis. Res. Ther. 12(1) , R4, (2010) Previous studies have shown that the number of myoblastically differentiated fibroblasts known as myofibroblasts (MFs) is significantly increased in stiff joint capsules, indicating their crucial role in the pathogenesis of post-traumatic joint stiffness. Alt... |
|
|
Role of prostaglandins in delayed cerebral ischemia after subarachnoid hemorrhage.
Neurosurgery 30(1) , 17-22, (1992) Prostaglandin E2, thromboxane B2, and 6-oxo-prostaglandin F1 alpha were assayed in blood and cerebrospinal fluid samples from patients after subarachnoid hemorrhage (SAH) and from a control population. The levels found in samples obtained from patients after ... |
|
|
Aspirin inhibits fractalkine expression in atherosclerotic plaques and reduces atherosclerosis in ApoE gene knockout mice.
Cardiovasc. Drugs Ther. 24(1) , 17-24, (2010) To determine the fractalkine expression in the aorta of ApoE (-/-) mice and the effect of high-dose aspirin intervention on fractalkine expression and atherosclerotic lesion formation.Twenty-one male ApoE gene knockout mice were randomized into three groups t... |
|
|
Effects of pathological flow on pulmonary artery endothelial production of vasoactive mediators and growth factors.
J. Vasc. Res. 46(6) , 561-71, (2009) Alterations in pulmonary blood flow are often associated with the initiation and progression of pulmonary vascular disease. However, the cellular mechanisms involved in mediating flow effects in the pulmonary circulation remain unclear. Depending on the disea... |
|
|
Design and synthesis of 4-O-methylhonokiol analogs as inhibitors of cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) and PGF₁ production.
Bioorg. Med. Chem. 20(9) , 2860-8, (2012) A series of novel 4-O-methylhonokiol analogs were synthesized in light of revealing structure-activity relationship for inhibitory effect of COX-2 enzyme. The key strategy of the molecular design was oriented towards modification of the potential metabolic so... |
|
|
Unusual metabolism of prostacyclin in infants with persistent septic pulmonary hypertension.
Eicosanoids 3(4) , 237-42, (1990) In urine of healthy man, the major metabolite of prostacyclin is 2,3-dinor-6-oxo-prostaglandin F1 alpha. The excretion rates of this compound as well as of 2,3-dinor-thromboxane B2, a major metabolite of thromboxane A2, in two newborns with septic persistent ... |
|
|
Selective cyclooxygenase inhibition improves hepatic encephalopathy in fulminant hepatic failure of rat.
Eur. J. Pharmacol. 666(1-3) , 226-32, (2011) Prostaglandin plays an important role in the pathogenesis of hepatic encephalopathy. This study investigated the therapeutic effects of selective cyclooxygenase (COX) inhibitor on hepatic encephalopathy in thioacetamide-induced fulminant hepatic failure (FHF)... |