Chaetoglobosin A
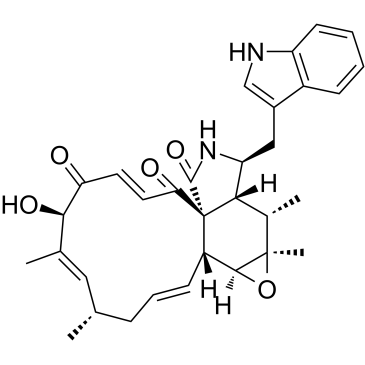
Chaetoglobosin A structure
|
Common Name | Chaetoglobosin A | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 50335-03-0 | Molecular Weight | 528.63900 | |
| Density | 1.3 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 789.7ºC at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C32H36N2O5 | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | N/A | Flash Point | 431.4ºC | |
|
Exploiting the cytoskeletal filaments of neoplastic cells to potentiate a novel therapeutic approach.
Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1846(2) , 599-616, (2014) Although cytoskeletal-directed agents have been a mainstay in chemotherapeutic protocols due to their ability to readily interfere with the rapid mitotic progression of neoplastic cells, they are all microtubule-based drugs, and there has yet to be any microf... |
|
|
Chaetoglobosin K induces apoptosis and G2 cell cycle arrest through p53-dependent pathway in cisplatin-resistant ovarian cancer cells.
Cancer Lett. 356(2 Pt B) , 418-33, (2015) Adverse side effects and acquired resistance to conventional platinum based chemotherapy have become major impediments in ovarian cancer treatment, and drive the development of more selective anticancer drugs. Chaetoglobosin K (ChK) was shown to have a more p... |
|
|
Chaetoglobosin F, a small molecule compound, possesses immunomodulatory properties on bone marrow-derived dendritic cells via TLR9 signaling pathway.
Immunobiology 218(3) , 292-302, (2013) Chaetoglobosin F (Cha F), a cytochalasan-based alkaloid, was obtained from the EtOAc extract of a solid culture of Chaetomium globosum IFB-E019. Dendritic cells (DCs), the most potent antigen presenting cells, are considered as the major target in the modulat... |
|
|
Protective effect of the natural product, chaetoglobosin K, on lindane- and dieldrin-induced changes in astroglia: identification of activated signaling pathways.
Pharm. Res. 25(6) , 1297-308, (2008) The purpose of the present study was to identify the biochemical mechanism(s) of the preventative and reversal effects of Chaetoglobosin K (ChK), a bioactive natural product, on inhibition of gap junction-mediated communication and connexin phosphorylation by... |
|
|
Growth and mycotoxin production by Chaetomium globosum.
Mycopathologia 164(1) , 49-56, (2007) Chaetomium globosum, the most common species within this genus, produces chaetoglobosins A and C when cultured on building material. Relatively low levels of these compounds have been shown to be lethal to various tissue culture cell lines. This study had two... |
|
|
Electrospray ionization tandem mass spectrometry of chaetoglobosins.
Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 26(18) , 2115-22, (2012) Chaetoglobosins are a family of macrocyclic polyketide alkaloids. They possess many similar isomers and exhibit a wide range of biological activities. Thus, there is a need for reliable, fast, and low-cost analysis of this class of compounds.A series of seven... |
|
|
Prevention of organochlorine-induced inhibition of gap junctional communication by chaetoglobosin K in astrocytes.
Cell Biol. Toxicol. 17(6) , 395-408, (2001) Innumerable toxic substances present in the environment inhibit gap junctions, intercellular membrane channels that play fundamental roles in coordinated function of cells and tissues. Included are persistent organochlorine compounds, which pose health risks ... |
|
|
Chaetoglobosin Fex from the marine-derived endophytic fungus inhibits induction of inflammatory mediators via Toll-like receptor 4 signaling in macrophages.
Biol. Pharm. Bull. 34(12) , 1864-73, (2011) Chaetoglobosin Fex (Cha Fex), a cytochalasan-based alkaloid, was isolated from marine-derived endophytic fungus Chaetomium globosum QEN-14. The knowledge of its biological function is still limited. We investigated the effects and mechanism of Cha Fex on infl... |
|
|
Cytotoxic 10-(indol-3-yl)-[13]cytochalasans from the fungus Chaetomium elatum ChE01.
Arch. Pharm. Res. 33(8) , 1135-41, (2010) Nine 10-(indol-3-yl)-[13]cytochalasans such as a new chaetoglobosin V (1); two new natural products, prochaetoglobosin III (2) and prochaetoglobosin III(ed) (3); six known chaetoglobosins B-D (4-6), F (7), and G (8) and isochaetoglobosin D (9) in addition to ... |
|
|
Enhancement of fibrinolytic activity of vascular endothelial cells by chaetoglobosin A, crinipellin B, geodin and triticone B.
J. Antibiot. 53(3) , 262-8, (2000) Four fungal metabolites, chaetoglobosin A (CGA), crinipellin B (CPB), geodin (GE) and triticone B (TTB), were found to enhance fibrinolytic activity of bovine aortic endothelial cells. Plasmin generation on the cells was elevated 2- to 4-fold when treated wit... |