N-p-Tosyl-Gly-Pro-Lys-pNA (acetate)
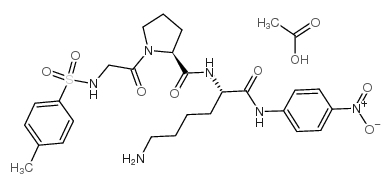
N-p-Tosyl-Gly-Pro-Lys-pNA (acetate) structure
|
Common Name | N-p-Tosyl-Gly-Pro-Lys-pNA (acetate) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 88793-79-7 | Molecular Weight | 634.70100 | |
| Density | N/A | Boiling Point | 966.2ºC at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C28H38N6O9S | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | USA | Flash Point | 538.1ºC | |
|
Assay of coagulation proteases using peptide chromogenic and fluorogenic substrates.
Meth. Enzymol. 80 , 341, (1981)
|
|
|
Streptococcus pneumoniae choline-binding protein E interaction with plasminogen/plasmin stimulates migration across the extracellular matrix.
Infect. Immun. 76 , 466-76, (2008) The virulence mechanisms leading Streptococcus pneumoniae to convert from nasopharyngeal colonization to a tissue-invasive phenotype are still largely unknown. Proliferation of infection requires penetration of the extracellular matrix, which occurs by recrui... |
|
|
Properties of PASP: a Pseudomonas protease capable of mediating corneal erosions.
Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 50 , 3794-801, (2010) To analyze PASP in terms of its gene distribution and expression, its corneal pathologic effects, its enzymatic properties, and the protectiveness of the immune response to this protease.Twenty-five strains of P. aeruginosa were analyzed for the PASP gene and... |
|
|
A bi-functional anti-thrombosis protein containing both direct-acting fibrin(ogen)olytic and plasminogen-activating activities.
PLoS ONE 6 , e17519, (2011) Direct-acting fibrin(ogen)olytic agents such as plasmin have been proved to contain effective and safety thrombolytic potential. Unfortunately, plasmin is ineffective when administered by the intravenous route because it was neutralized by plasma antiplasmin.... |