Chlorhexidine Dihydrochloride
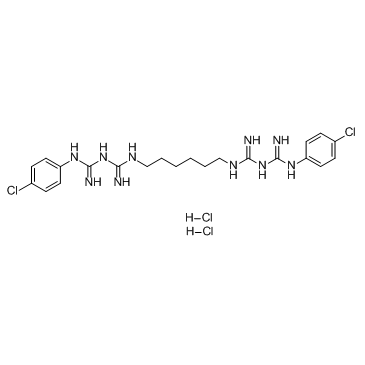
Chlorhexidine Dihydrochloride structure
|
Common Name | Chlorhexidine Dihydrochloride | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 3697-42-5 | Molecular Weight | 578.369 | |
| Density | N/A | Boiling Point | 699.3ºC at 760mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C22H32Cl4N10 | Melting Point | 255-262 ºC | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 376.7ºC | |
|
Evaluation of preventive programs in high caries active preschool children.
Swed. Dent. J. 37(1) , 23-9, (2013) Although caries prevalence in preschool children has dramatically decreased during the last decades it is still a large problem for a minor group of these children. Great efforts have been invested in finding effective preventive programs for the high caries ... |
|
|
Effect of irrigation with Tetraclean on bacterial leakage of obturated root canals.
N. Y. State Dent. J. 80(3) , 39-43, (2014) The purpose of the study presented here was to evaluate the effect of Tetraclean, Hypoclean, Chlor-XTRA, 2% chlorhexidine and 6% sodium hypochlorite/17% EDTA as a final irrigant on bacterial leakage of the root canal. One hundred and fifty-five extracted huma... |
|
|
Short-term decline in all-cause acquired infections with the routine use of a decontamination regimen combining topical polymyxin, tobramycin, and amphotericin B with mupirocin and chlorhexidine in the ICU: a single-center experience.
Crit. Care Med. 42(5) , 1121-30, (2014) In a multicenter, placebo-controlled, randomized, double-blind trial, we showed that acquired infections in intubated patients were reduced by the combination of topical polymyxin plus tobramycin and nasal mupirocin plus chlorhexidine body wash. Because intub... |
|
|
A prospective clinical evaluation of the longevity of resorbable sutures in oral surgical procedures.
Niger. J. Clin. Pract. 16(3) , 334-8, (2013) The objectives of this prospective randomized study were to clinically evaluate the longevity of resorbable sutures (chromic catgut and vicryl) and determine the effect of chlorhexidine mouth wash on their absorption time in oral surgical procedures. Both sut... |
|
|
Antibacterial dental composites with chlorhexidine and mesoporous silica.
J. Dent. Res. 93(12) , 1283-9, (2014) One of the leading causes for the failure of dental composite restorations is secondary caries. Effectively inhibiting cariogenic biofilms and reducing secondary caries could extend the service life of composite restorations. Dental composites releasing antib... |
|
|
Alcohol plus chlorhexidine is more efficient than alcohol alone for phenol-based chemical matricectomy: an in vitro study.
Dermatol. Surg. 39(9) , 1363-7, (2013) A phenolization approach is often chosen for treatment of ingrown toenails. Many reports describe lavage of the wound with alcohol to neutralize any residual phenol. The aim of our study was to compare the suitability and effectiveness of a solution consistin... |
|
|
Commentary: Alcohol plus chlorhexidine is more efficient than alcohol alone for phenol-based chemical matricectomy: in vitro study.
Dermatol. Surg. 39(9) , 1368-9, (2013)
|
|
|
Cement-associated signs of inflammation: retrospective analysis of the effect of excess cement on peri-implant tissue.
Int. J. Prosthodont. 28(1) , 11-8, (2015) Excess cement left in the peri-implant sulcus after the placement of prosthetic restorations risks inflammation in the peri-implant tissue. While many current studies deal with the question of how to avoid undetected excess cement, relatively little is known ... |
|
|
Superficial roughness on composite surface, composite enamel and composite dentin junctions after different finishing and polishing procedures. Part I: roughness after treatments with tungsten carbide vs diamond burs.
Int. J. Esthet. Dent. 9(1) , 70-89, (2014) The aim of this study is to investigate different instruments for finishing composite restorations, as well as examining different surfaces and interfaces of the same restoration. The null hypothesis is represented by the fact that there are no significant di... |
|
|
Determining the minimum inhibitory concentration of Tetraclean against Candida albicans.
Niger. J. Med. 23(3) , 201-6, (2014) The purpose of the present study was to determine the minimum inhibitory concentrations of Tetraclean, chlorhexidine, hydrogen peroxide, and sodium hypochlorite against Candida albicans.Amphotericin B was used as positive control and RPMI plus 1 ml Candida su... |