DL-Sulforaphane
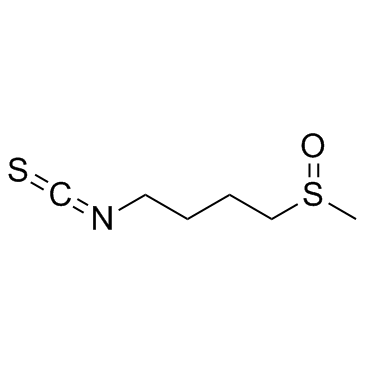
DL-Sulforaphane structure
|
Common Name | DL-Sulforaphane | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 4478-93-7 | Molecular Weight | 177.288 | |
| Density | 1.2±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 368.2±25.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C6H11NOS2 | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 176.5±23.2 °C | |
|
Novel Nrf2 activators from microbial transformation products inhibit blood-retinal barrier permeability in rabbits.
Br. J. Pharmacol. 172(5) , 1237-49, (2015) Nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 (Nrf2) is a redox-sensitive transcription factor that binds to antioxidant response elements located in the promoter region of genes encoding many antioxidant enzymes and phase II detoxifying enzymes. Activation of ... |
|
|
Sulforaphane reduces molecular response to hypoxia in ovarian tumor cells independently of their resistance to chemotherapy.
Int. J. Oncol. 47 , 51-60, (2015) One of the recently emerging anticancer strategies is the use of natural dietary compounds, such as sulforaphane, a cancer-chemopreventive isothiocyanate found in broccoli. Based on the growing evidence, sulforaphane acts through molecular mechanisms that int... |
|
|
A phase II study of sulforaphane-rich broccoli sprout extracts in men with recurrent prostate cancer.
Invest. New Drugs 33(2) , 480-9, (2015) Diets high in cruciferous vegetables are associated with lower risk of incidence of prostate cancer, including aggressive forms of this disease. Human intervention studies with cruciferous vegetable-rich diets also demonstrate modulation of gene expression in... |
|
|
Stimulation of suicidal erythrocyte death by sulforaphane.
Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol. 116(3) , 229-35, (2015) Sulforaphane, an isothiocyanate from cruciferous vegetable, counteracts malignancy. The effect is at least in part due to the stimulation of suicidal death or apoptosis of tumour cells. Mechanisms invoked in sulforaphane-induced apoptosis include mitochondria... |
|
|
Pregnane X receptor activation and silencing promote steatosis of human hepatic cells by distinct lipogenic mechanisms.
Arch. Toxicol. 89 , 2089-103, (2015) In addition to its well-characterized role in the regulation of drug metabolism and transport by xenobiotics, pregnane X receptor (PXR) critically impacts on lipid homeostasis. In mice, both ligand-dependent activation and knockout of PXR were previously show... |
|
|
Aspalathin and nothofagin from rooibos (Aspalathus linearis) inhibit endothelial protein C receptor shedding in vitro and in vivo.
Fitoterapia 100 , 179-86, (2015) Aspalathin (Asp) and nothofagin (Not) are two major active dihydrochalcones found in green rooibos, which have been reported for their anti-oxidant activity. Increasing evidence has demonstrated that beyond its role in the activation of protein C, endothelial... |
|
|
SUV39H1/H3K9me3 attenuates sulforaphane-induced apoptotic signaling in PC3 prostate cancer cells.
Oncogenesis 3 , e131, (2014) The isothiocyanate sulforaphane is a promising molecule for development as a therapeutic agent for patients with metastatic prostate cancer. Sulforaphane induces apoptosis in advanced prostate cancer cells, slows disease progression in vivo and is well tolera... |
|
|
Nrf2 regulates PU.1 expression and activity in the alveolar macrophage.
Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 308 , L1086-93, (2015) Alveolar macrophage (AM) immune function depends on the activation of the transcription factor PU.1 by granulocyte macrophage colony-stimulating factor. We have determined that chronic alcohol ingestion dampens PU.1 signaling via an unknown zinc-dependent mec... |
|
|
Baicalein Decreases Hydrogen Peroxide-Induced Damage to NG108-15 Cells via Upregulation of Nrf2.
J. Cell Physiol. 230 , 1840-51, (2015) Baicalein is a flavonoid inhibitor of 12-lipoxygenase. Here, we investigated its effect on hydrogen peroxide-induced damage to NG108-15 cells. Hydrogen peroxide activated the mitochondrial apoptotic pathway, decreased Nrf2 expression, increased reactive oxyge... |
|
|
NRF2 Regulates PINK1 Expression under Oxidative Stress Conditions.
PLoS ONE 10 , e0142438, (2015) Mutations of the PTEN-induced putative kinase 1 (PINK1) gene are a cause of autosomal recessive forms of Parkinson's disease. Recent studies have revealed that PINK1 is an essential factor for controlling mitochondrial quality, and that it protects cells from... |