Flupirtine maleate
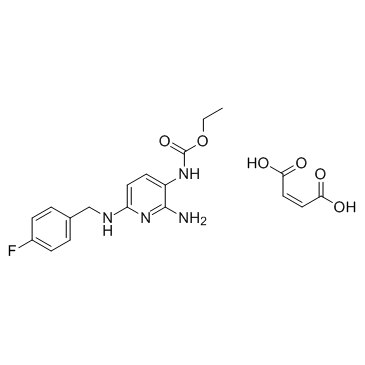
Flupirtine maleate structure
|
Common Name | Flupirtine maleate | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 75507-68-5 | Molecular Weight | 420.392 | |
| Density | 1.35 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 434.9ºC at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C19H21FN4O6 | Melting Point | 186-188ºC | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 216.8ºC | |
|
Role of Kv7 channels in responses of the pulmonary circulation to hypoxia.
Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 308(1) , L48-57, (2015) Hypoxic pulmonary vasoconstriction (HPV) is a beneficial mechanism that diverts blood from hypoxic alveoli to better ventilated areas of the lung, but breathing hypoxic air causes the pulmonary circulation to become hypertensive. Responses to airway hypoxia a... |
|
|
M channel enhancers and physiological M channel block.
J. Physiol. 590(Pt 4) , 793-807, (2012) M-type (Kv7, KCNQ) K(+) channels control the resting membrane potential of many neurons, including peripheral nociceptive sensory neurons. Several M channel enhancers were suggested as prospective analgesics, and targeting M channels specifically in periphera... |
|
|
M-type potassium channels modulate Schaffer collateral-CA1 glutamatergic synaptic transmission.
J. Physiol. 590(Pt 16) , 3953-64, (2012) Previous studies have suggested that muscarinic receptor activation modulates glutamatergic transmission. M-type potassium channels mediate the effects of muscarinic activation in the hippocampus, and it has been proposed that they modulate glutamatergic syna... |
|
|
Flupirtine, a re-discovered drug, revisited.
Inflamm. Res. 62(3) , 251-8, (2013) Flupirtine was developed long before K(V)7 (KCNQ) channels were known. However, it was clear from the beginning that flupirtine is neither an opioid nor a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory analgesic. Its unique muscle relaxing activity was discovered by serendip... |
|
|
Parent-reported benefits of flupirtine in juvenile neuronal ceroid lipofuscinosis (Batten disease; CLN3) are not supported by quantitative data.
J. Inherit. Metab. Dis. 34(5) , 1075-81, (2011) Juvenile neuronal ceroid lipofuscinosis (JNCL; CLN3 disease; Batten disease) is an autosomal recessive neurodegenerative disease of childhood that typically presents at school age with vision loss followed by progressive cognitive decline, motor dysfunction, ... |
|
|
Protective effect of the KCNQ activator flupirtine on a model of repetitive febrile seizures
Epilepsy Res. 97(1-2) , 64-72, (2011) Activation of KCNQ-channels has been shown to decrease or reduce the propagation of neuronal excitation in the immature central nervous system, and KCNQ activators represent a new class of anticonvulsant compounds. Their effectiveness has been demonstrated in... |
|
|
Flupirtine inhibits calcitonin-gene related peptide release from rat brainstem in vitro.
Neurosci. Lett. 506(2) , 332-5, (2012) We have previously shown that the nonopioid analgesic flupirtine possesses analgesic activity in the orofacial formalin test in vivo in the rat. However, this paradigm does not allow to distinguish between central and peripheral site of action of the drug. In... |
|
|
Efficacy and tolerability of flupirtine in subacute/ chronic musculoskeletal pain - results of a patient level, pooled re-analysis of randomized, double-blind, controlled trials.
Int. J. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 49(11) , 637-47, (2011) Flupirtine, a nonopioid analgesic without antipyretic or antiphlogistic properties, constitutes a unique class within the group of WHO-I analgesics. First approved in Germany on a national level in 1989, this selective neuronal potassium channel opener evolve... |
|
|
Bioanalytical method development, validation and quantification of flupirtine maleate in rat plasma by liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry.
Arzneimittelforschung 61(12) , 693-9, (2011) A simple, highly sensitive, precise and accurate high-performance liquid chromatographic (LCMSMS) method with mass detection was developed and validated for the rapid quantification of flupirtine (CAS 75507-68-5) in rat plasma samples. The chromatographic sep... |
|
|
Flupirtine-induced hepatic failure requiring orthotopic liver transplant.
Exp. Clin. Transplant. 9(4) , 270-2, (2011) We present the case of a 48-year-old otherwise healthy man who required an urgent liver transplant owing to acute liver failure after flupirtine treatment. After 3 months of daily flupirtine intake as treatment for pseudoradicular pain syndrome, he presented ... |