γ-D-Glutamylaminomethylsulfonic acid
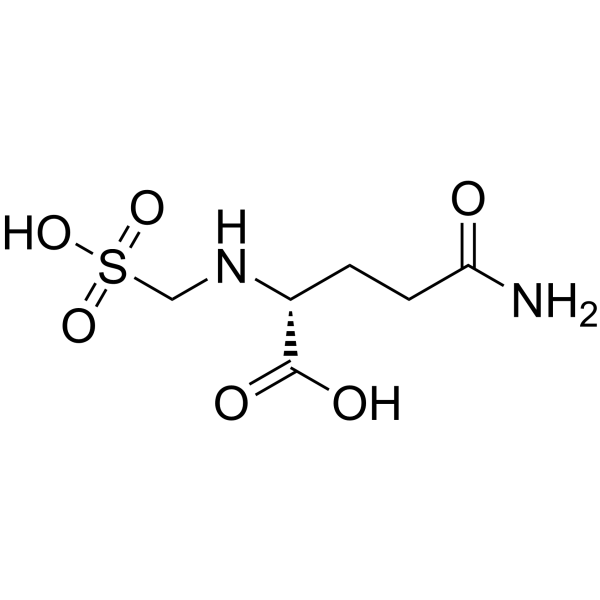
γ-D-Glutamylaminomethylsulfonic acid structure
|
Common Name | γ-D-Glutamylaminomethylsulfonic acid | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 90237-02-8 | Molecular Weight | 240.23400 | |
| Density | 1.593g/cm3 | Boiling Point | N/A | |
| Molecular Formula | C6H12N2O6S | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | USA | Flash Point | N/A | |
|
Effects of some excitatory amino acid antagonists on imipenem-induced seizures in DBA/2 mice.
Brain Res. 671(1) , 131-40, (1995) The behavioural and convulsant effects of imipenem (Imi), a carbapenem derivative, were studied after intraperitoneal (i.p.) or intracerebroventricular (i.c.v.) administration in DBA/2 mice, a strain genetically susceptible to sound-induced seizures. The anti... |
|
|
Glutamate and vasopressin interact to control scent marking in Syrian hamsters (Mesocricetus auratus).
Brain Res. 731(1-2) , 213-6, (1996) In Syrian hamsters, vasopressin (AVP) in the medial preoptic-anterior hypothalamus (MPOA-AH) controls a form of scent marking called flank marking. Another neurochemical signal that may interact with AVP to control flank marking is glutamate. We tested the hy... |
|
|
Excitatory neurotransmitters in the lateral habenula and pedunculopontine nucleus of rat modulate limbic seizures induced by pilocarpine.
Brain Res. 591(2) , 209-22, (1992) The involvement of the excitatory neurotransmitter system in the lateral habenula and pedunculopontine nucleus in the initiation and propagation of limbic seizures induced by pilocarpine has been investigated in the rat. Limbic seizures occur in animals follo... |
|
|
Evidence for an involvement of NMDA and non-NMDA receptors in synaptic excitation of phrenic motoneurons in the rabbit.
Neurosci. Lett. 130(2) , 271-4, (1991) The action of endogenous excitatory amino acids on phrenic motoneurons was studied in anesthetized, vagotomized, paralyzed and artificially ventilated rabbits. The NMDA receptor antagonists APV and ketamine, as well as the non-NMDA receptor antagonists GAMS a... |
|
|
Release of GABA from sensory neurons transduced with a GAD67-expressing vector occurs by non-vesicular mechanisms.
Brain Res. 1073-1074 , 297-304, (2006) We have demonstrated that dorsal root ganglion neurons transduced with a recombinant replication-defective herpes simplex virus vector coding for glutamic acid decarboxylase (QHGAD67) release GABA to produce an analgesic effect in rodent models of pain. In th... |
|
|
Preferential block of desensitizing AMPA receptor in hippocampal neurons by gamma-D-glutamylaminomethylsulfonic acid.
Eur. J. Pharmacol. 284 , 141-147, (1995) The (RS)-alpha-Amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazolopropionic acid (AMPA)/kainate receptor-channel complex mediates fast components of excitatory synaptic currents in the central nervous system. Distinguishing between these components is a difficult pharmacolo... |
|
|
2-APV and DGAMS are superior to MK-801 in preventing hypoxia-induced injury to developing neurons in vitro.
Pediatr. Neurol. 7(6) , 429-35, (1991) The relative efficacy of competitive and noncompetitive excitatory amino acid antagonists in preventing hypoxic neuronal injury recently was examined in vitro. Immature (26 days post-conception) fetal mouse cerebral cortical cell cultures were exposed 10 days... |
|
|
Role of neuronal NMDA and non-NMDA glutamate receptors in medial vestibular nucleus in the regulation of respiratory rhythmogenesis in newborn rats in vitro.
Bull. Exp. Biol. Med. 148(2) , 167-70, (2009) We studied isolated pontobulbospinal preparations from newborn rat brain. In the early postnatal period, the rostral part of the medial vestibular nucleus produces a potent inhibitory effect on neuronal structures of the bulbar respiratory center via the glut... |
|
|
Role of NMDA- and non-NMDA subtypes of glutamate receptors in A5 neuronal structures in the regulation of respiration and circulation during thermal nociceptive stimulation in rats.
Bull. Exp. Biol. Med. 146(5) , 551-4, (2008) In narcotized albino rats, thermal nociceptive stimulation elevated systemic blood pressure and increased the frequency of respiratory rhythm generation. Unilateral microinjection of ketamine hydrochloride, a selective blocker for NMDA receptors, into A5 regi... |
|
|
Neurotoxic effects of excitatory amino acids in the mouse spinal cord: quisqualate and kainate but not N-methyl-D-aspartate induce permanent neural damage.
Brain Res. 529(1-2) , 7-15, (1990) Despite extensive evidence for the neurotoxic effects of excitatory amino acids (EAA) in the brain little is known about their neurotoxic action in the spinal cord. In this study we attempted to produce differential lesions of spinal neurons by pretreating mi... |