Bafilomycin A1
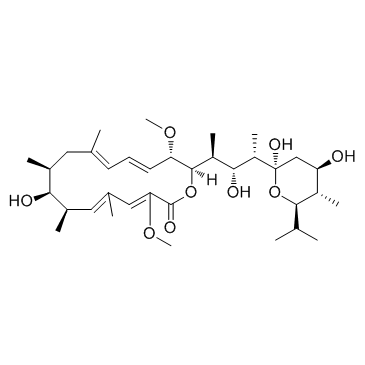
Bafilomycin A1 structure
|
Common Name | Bafilomycin A1 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 88899-55-2 | Molecular Weight | 622.830 | |
| Density | 1.1±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 770.1±60.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C35H58O9 | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 232.2±26.4 °C | |
|
SUMO1 promotes Aβ production via the modulation of autophagy.
Autophagy 11(1) , 100-12, (2015) Autophagy is one of the main mechanisms in the pathophysiology of neurodegenerative disease. The accumulation of autophagic vacuoles (AVs) in affected neurons is responsible for amyloid-β (Aβ) production. Previously, we reported that SUMO1 (small ubiquitin-li... |
|
|
GA binding protein augments autophagy via transcriptional activation of BECN1-PIK3C3 complex genes.
Autophagy 10(9) , 1622-36, (2014) Macroautophagy is a vesicular catabolic trafficking pathway that is thought to protect cells from diverse stressors and to promote longevity. Recent studies have revealed that transcription factors play important roles in the regulation of autophagy. In this ... |
|
|
Autophagy facilitates secretion and protects against degeneration of the Harderian gland.
Autophagy 11(2) , 298-313, (2015) The epithelial derived Harderian gland consists of 2 types of secretory cells. The more numerous type A cells are responsible for the secretion of lipid droplets, while type B cells produce dark granules of multilamellar bodies. The process of autophagy is co... |
|
|
Defects in calcium homeostasis and mitochondria can be reversed in Pompe disease.
Autophagy 11(2) , 385-402, (2015) Mitochondria-induced oxidative stress and flawed autophagy are common features of neurodegenerative and lysosomal storage diseases (LSDs). Although defective autophagy is particularly prominent in Pompe disease, mitochondrial function has escaped examination ... |
|
|
Japanese encephalitis virus replication is negatively regulated by autophagy and occurs on LC3-I- and EDEM1-containing membranes.
Autophagy 10(9) , 1637-51, (2014) Autophagy is a lysosomal degradative pathway that has diverse physiological functions and plays crucial roles in several viral infections. Here we examine the role of autophagy in the life cycle of JEV, a neurotropic flavivirus. JEV infection leads to inducti... |
|
|
Endothelin-1 regulates H⁺-ATPase-dependent transepithelial H⁺ secretion in zebrafish.
Endocrinology 155(5) , 1728-37, (2014) Endothelin-1 (EDN1) is an important regulator of H⁺ secretion in the mammalian kidney. EDN1 enhances renal tubule H⁺-ATPase activity, but the underlying mechanism remains unclear. To further elucidate the role of EDN1 in vertebrates' acid-base regulation, the... |
|
|
Concurrent MEK and autophagy inhibition is required to restore cell death associated danger-signalling in Vemurafenib-resistant melanoma cells.
Biochem. Pharmacol. 93(3) , 290-304, (2015) Vemurafenib (PLX4032), an inhibitor of BRAF(V600E), has demonstrated significant clinical anti-melanoma effects. However, the majority of treated patients develop resistance, due to a variety of molecular mechanisms including MAPK reactivation through MEK. Th... |
|
|
G2019S LRRK2 mutant fibroblasts from Parkinson's disease patients show increased sensitivity to neurotoxin 1-methyl-4-phenylpyridinium dependent of autophagy.
Toxicology 324 , 1-9, (2014) Parkinson's disease (PD) is a neurodegenerative disorder of unknown etiology. It is considered as a multifactorial disease dependent on environmental and genetic factors. Deregulation in cell degradation has been related with a significant increase in cell da... |
|
|
Autophagy blockade sensitizes the anticancer activity of CA-4 via JNK-Bcl-2 pathway.
Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 274(2) , 319-27, (2014) Combretastatin A-4 (CA-4) has already entered clinical trials of solid tumors over ten years. However, the limited anticancer activity and dose-dependent toxicity restrict its clinical application. Here, we offered convincing evidence that CA-4 induced autoph... |
|
|
Mitigation of autophagy ameliorates hepatocellular damage following ischemia-reperfusion injury in murine steatotic liver.
Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 307(11) , G1088-99, (2014) Ischemia-reperfusion injury (IRI) is a common clinical consequence of hepatic surgery, cardiogenic shock, and liver transplantation. A steatotic liver is particularly vulnerable to IRI, responding with extensive hepatocellular injury. Autophagy, a lysosomal p... |