Dodecylbenzene
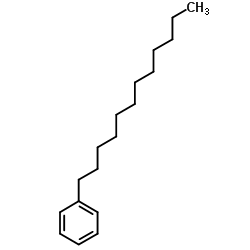
Dodecylbenzene structure
|
Common Name | Dodecylbenzene | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 123-01-3 | Molecular Weight | 246.431 | |
| Density | 0.9±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 331.4±5.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C18H30 | Melting Point | -7ºC | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 144.8±5.4 °C | |
|
Broad spectrum analysis of polar and apolar organic compounds in submicron atmospheric particles.
J. Chromatogr. A. 1404 , 28-38, (2015) A method for the quantitative analysis of organic compounds on submicron particulate matter (PM1) collected on quartz filters was developed. The compounds analyzed encompassed C22-C35 alkanes, polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs), quinones, levoglucosan, c... |
|
|
In situsynthesis of di-n-butyll-tartrate–boric acid complex chiral selector and its application in chiral microemulsion electrokinetic chromatography
J. Chromatogr. A. 1216(45) , 7932-40, (2009) A novel procedure for in situ assembling a complex chiral selector, di- n-butyl l-tartrate–boric acid complex, by the reaction of di- n-butyl l-tartrate with boric acid in a running buffer was reported and its application in the enantioseparation of β-blocker... |
|
|
The degradation of 1-phenylalkanes by an oil-degrading strain of Acinetobacter lwoffi.
Antonie van Leeuwenhoek 51(1) , 45-56, (1985) An oil-degrading bacterium identified as Acinetobacter lwoffi was isolated by elective culture on North Sea Forties crude oil from an activated sludge sample. It grew on a wide range of n-alkanes (C12-C28) and 1-phenylalkanes, including 1-phenyldodecane, 1-ph... |
|
|
Validation of an assay for the determination of levoglucosan and associated monosaccharide anhydrides for the quantification of wood smoke in atmospheric aerosol.
Anal. Bioanal. Chem 406(22) , 5283-92, (2014) Biomass burning is becoming an increasing contributor to atmospheric particulate matter, and concern is increasing over the detrimental health effects of inhaling such particles. Levoglucosan and related monosaccharide anhydrides (MAs) can be used as tracers ... |
|
|
Design and characterization of antimicrobial usnic acid loaded-core/shell magnetic nanoparticles.
Mater. Sci. Eng. C. Mater. Biol. Appl. 52 , 72-81, (2015) The application of magnetic nanoparticles (MNPs) in medicine is considered much promising especially because they can be handled and directed to specific body sites by external magnetic fields. MNPs have been investigated in magnetic resonance imaging, hypert... |
|
|
[Effect of surfactant on the evaporation of BTEX from static water].
Huan Jing Ke Xue 26(1) , 122-6, (2005) Effect of surfactant on the evaporative loss of benzene, toluene and ethylbenzene from static water was researched and the mechanism of surfactant was studied, so as try to supply theoretical reference for the effect of surfactant on the evaporation of comple... |
|
|
Copper-catalyzed arylation of amines using diphenyl pyrrolidine-2-phosphonate as the new ligand.
J. Org. Chem. 70(20) , 8107-9, (2005) [Chemical reaction: See text] We have developed a general, efficient, and inexpensive catalyst system for arylation of amines by using 10 mol % of CuI as the copper source, 20 mol % of diphenyl pyrrolidine-2-phosphonate (DPP) as the ligand, K3PO4 as the base,... |
|
|
Studies of the carcinogenesis and tumorigenesis of skin applications of dodecylbenzene on hairless mice.
Br. J. Ind. Med. 46(9) , 608-16, (1989) Dodecylbenzene in various concentrations, dissolved in acetone to a final volume of 50 microliters, was applied twice a week for 78 weeks to the back skin of hairless mice, with or without pretreatment with 51.2 micrograms 9,10-dimethyl-1,2-benzanthracene (DM... |
|
|
Study of adjuvant effect of model surfactants from the groups of alkyl sulfates, alkylbenzene sulfonates, alcohol ethoxylates and soaps.
Food Chem. Toxicol. 38(11) , 1065-74, (2000) The sodium salts of representatives of anionic surfactants, dodecylbenzene sulfonate (SDBS), dodecyl sulfate (SDS) and coconut oil fatty acids, and a nonionic surfactant, dodecyl alcohol ethoxylate, were studied for adjuvant effect on the production of specif... |
|
|
The branched-chain dodecylbenzene sulfonate degradation pathway of Pseudomonas aeruginosa W51D involves a novel route for degradation of the surfactant lateral alkyl chain.
Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 65(8) , 3730-4, (1999) Pseudomonas aeruginosa W51D is able to grow by using branched-chain dodecylbenzene sulfonates (B-DBS) or the terpenic alcohol citronellol as a sole source of carbon. A mutant derived from this strain (W51M1) is unable to degrade citronellol but still grows on... |