Basic Brown 1
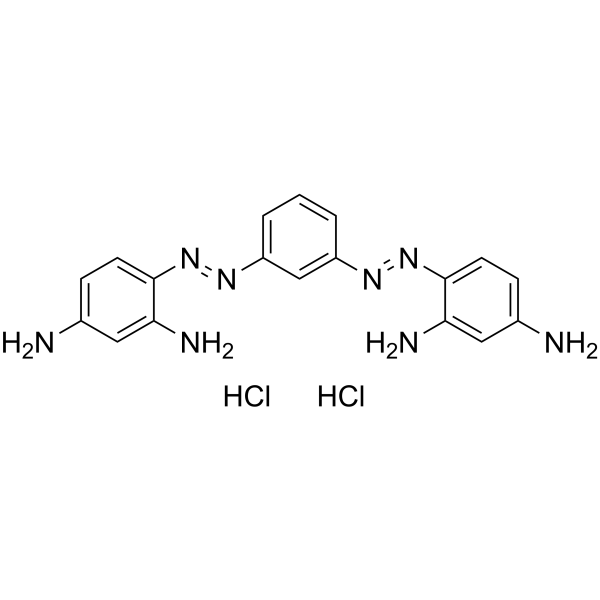
Basic Brown 1 structure
|
Common Name | Basic Brown 1 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 10114-58-6 | Molecular Weight | 419.311 | |
| Density | 1.42g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 696.4ºC at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C18H20Cl2N8 | Melting Point | 220ºC | |
| MSDS | USA | Flash Point | N/A | |
|
Analysis and testing of biological stains--the Biological Stain Commission Procedures.
Biotech. Histochem. 77(5&6) , 237-275, (2002)
|
|
|
Papanicolaou staining--a review.
Microsc. Acta 87(3) , 233-43, (1983) Some technical aspects of Papanicolaou staining are reviewed. The history of the technique is traced from Mallory's aniline blue technique through Masson's trichrome procedure to the techniques of Shorr. The histochemistry of the three Papanicolaou staining s... |
|
|
Plant cuticle staining with bismarck brown Y and azure B or toluidine blue O before paraffin extraction.
Biotech. Histochem. 71(2) , 92-5, (1996) Transverse paraffin sections of mature greenwood stems of rose (Rosa x hybrida) and flowering dogwood (Cornus florida L.) were stained with Bismarck brown followed by azure B or toluidine blue 0. The Bismarck brown was replaced by thiazin dye metachromasia in... |
|
|
[Case of poisoning by the dye Bismark Brown].
Sud. Med. Ekspert. 29(3) , 59, (1986)
|
|
|
Prediction of optimum sorption isotherm: comparison of linear and non-linear method.
J. Hazard. Mater. 126(1-3) , 198-201, (2005) Equilibrium parameters for Bismarck brown onto rice husk were estimated by linear least square and a trial and error non-linear method using Freundlich, Langmuir and Redlich-Peterson isotherms. A comparison between linear and non-linear method of estimating t... |
|
|
Enzymatic grafting of carboxyl groups on to chitosan--to confer on chitosan the property of a cationic dye adsorbent.
Bioresour. Technol. 91(2) , 157-62, (2004) Chitosan (CTS) is a good adsorbent for dyes but lacks the ability to adsorb cationic dyes. In this study, chitosan was modified to possess the ability to adsorb cationic dyes from water. Four kinds of phenol derivatives: 4-hydroxybenzoic acid (BA), 3,4-dihydr... |
|
|
Preparation of steam activated carbon from rubberwood sawdust (Hevea brasiliensis) and its adsorption kinetics.
J. Hazard. Mater. 136(3) , 922-9, (2006) Activated carbon was produced from a biowaste product, rubberwood sawdust (RWSD) using steam in a high temperature fluidized bed reactor. Experiments were carried out to investigate the influence of various process parameters such as activation time, activati... |
|
|
Adsorption of Bismark Brown dye on activated carbons prepared from rubberwood sawdust (Hevea brasiliensis) using different activation methods.
J. Hazard. Mater. 126(1-3) , 63-70, (2005) Hevea brasiliensis or rubberwood tree, as it is commonly known finds limited use once the latex has been tapped. The sawdust of this tree is chosen to ascertain it viability as a precursor for activation. The carbons thus obtained were characterized in terms ... |
|
|
Use of a triple-stain technique to detect viability and acrosome reaction in deer spermatozoa.
Arch. Androl. 39(1) , 1-9, (1997) A procedure is described for simultaneously evaluating of sperm viability and acrosomal status in fixed deer spermatozoa. This technique, which is a modification of the triple-stain technique (TST) developed for human sperm, utilizes trypan blue to identify t... |
|
|
Assessment of the joint effect of laccase and cellobiose dehydrogenase on the decolouration of different synthetic dyes.
J. Hazard. Mater. 169(1-3) , 176-81, (2009) In this paper the efficiency of the combined action of laccase and cellobiose dehydrogenase (CDH) to decolourise different synthetic dyes such as Remazol Brilliant Blue R (RBBR), Methyl Green (MG), Direct Violet (DV), Ponceau Xylidine (PX), Bismark Brown (BB)... |