Phosphoenolpyruvic acid cyclohexylammonium salt
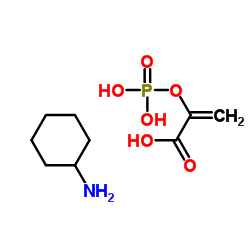
Phosphoenolpyruvic acid cyclohexylammonium salt structure
|
Common Name | Phosphoenolpyruvic acid cyclohexylammonium salt | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 10526-80-4 | Molecular Weight | 267.216 | |
| Density | N/A | Boiling Point | 466.7ºC at 760mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C9H18NO6P | Melting Point | 140°C | |
| MSDS | USA | Flash Point | 236.1ºC | |
|
The PEP-pyruvate-oxaloacetate node as the switch point for carbon flux distribution in bacteria.
FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 29(4) , 765-94, (2005) In many organisms, metabolite interconversion at the phosphoenolpyruvate (PEP)-pyruvate-oxaloacetate node involves a structurally entangled set of reactions that interconnects the major pathways of carbon metabolism and thus, is responsible for the distributi... |
|
|
Inducer exclusion in Escherichia coli by non-PTS substrates: the role of the PEP to pyruvate ratio in determining the phosphorylation state of enzyme IIAGlc.
Mol. Microbiol. 30(3) , 487-98, (1998) The main mechanism causing catabolite repression in Escherichia coli is the dephosphorylation of enzyme IIAGlc, one of the enzymes of the phosphoenolpyruvate:carbohydrate phosphotransferase system (PTS). The PTS is involved in the uptake of a large number of ... |
|
|
Metabolic flux responses to pyruvate kinase knockout in Escherichia coli.
J. Bacteriol. 184(1) , 152-64, (2002) The intracellular carbon flux distribution in wild-type and pyruvate kinase-deficient Escherichia coli was estimated using biosynthetically directed fractional 13C labeling experiments with [U-13C6]glucose in glucose- or ammonia-limited chemostats, two-dimens... |
|
|
Metabolic pathway alterations that support cell proliferation.
Cold Spring Harb. Symp. Quant. Biol. 76 , 325-34, (2011) Proliferating cells adapt metabolism to support the conversion of available nutrients into biomass. How cell metabolism is regulated to balance the production of ATP, metabolite building blocks, and reducing equivalents remains uncertain. Proliferative metabo... |
|
|
In vivo analysis of metabolic dynamics in Saccharomyces cerevisiae : I. Experimental observations.
Biotechnol. Bioeng. 55(2) , 305-16, (1997) The goal of this work was to obtain rapid sampling technique to measure transient metabolites in vivo. First, a pulse of glucose was added to a culture of the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae growing aerobically under glucose limitation. Next, samples were remo... |
|
|
Multifunctional roles of enolase in Alzheimer's disease brain: beyond altered glucose metabolism.
J. Neurochem. 111(4) , 915-33, (2009) Enolase enzymes are abundantly expressed, cytosolic carbon-oxygen lyases known for their role in glucose metabolism. Recently, enolase has been shown to possess a variety of different regulatory functions, beyond glycolysis and gluconeogenesis, associated wit... |
|
|
The role of phosphometabolites in cell proliferation, energy metabolism, and tumor therapy.
J. Bioenerg. Biomembr. 29(4) , 315-30, (1997) A common characteristic of tumor cells is the constant overexpression of glycolytic and glutaminolytic enzymes. In tumor cells the hyperactive hexokinase and the partly inactive pyruvate kinase lead to an expansion of all phosphometabolites from glucose 6-pho... |
|
|
Robust control of PEP formation rate in the carbon fixation pathway of C(4) plants by a bi-functional enzyme.
BMC Syst. Biol. 5 , 171, (2011) C(4) plants such as corn and sugarcane assimilate atmospheric CO(2) into biomass by means of the C(4) carbon fixation pathway. We asked how PEP formation rate, a key step in the carbon fixation pathway, might work at a precise rate, regulated by light, despit... |
|
|
Rewiring of glycolysis in cancer cell metabolism.
Cell Cycle 9(21) , 4253, (2010)
|
|
|
Biosynthesis of aromatic amino acids by highly purified spinach chloroplasts. Compartmentation and regulation of the reactions. Bagge, P. and Larsson, C.
Physiol. Plant. 68 , 641-647, (1986)
|