4-Methylumbelliferone
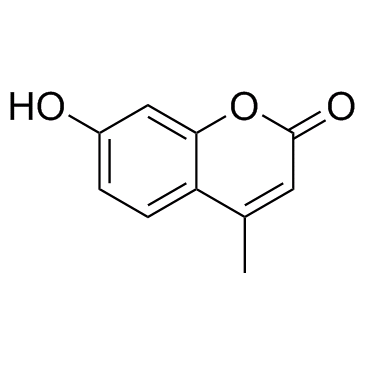
4-Methylumbelliferone structure
|
Common Name | 4-Methylumbelliferone | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 90-33-5 | Molecular Weight | 176.16900 | |
| Density | 1.319 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 377.4ºC at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C10H8O3 | Melting Point | 188.5-190 °C(lit.) | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 174.5ºC | |
|
Placental profiling of UGT1A enzyme expression and activity and interactions with preeclampsia at term.
Eur. J. Drug Metab. Pharmacokinet. 40 , 471-80, (2015) Placental UDP-glucuronosyltransferase (UGT) enzymes have critical roles in hormone, nutrient, chemical balance and fetal exposure during pregnancy. Placental UGT1A isoforms were profiled and differences between preeclamptic (PE) and non-PE placental UGT expre... |
|
|
Cell protrusions induced by hyaluronan synthase 3 (HAS3) resemble mesothelial microvilli and share cytoskeletal features of filopodia.
Exp. Cell Res. 337 , 179-91, (2015) Previous studies have shown that overexpression of enzymatically active GFP-HAS induces the growth of long, slender protrusions that share many features of both filopodia and microvilli. These protrusions are dependent on continuing hyaluronan synthesis, and ... |
|
|
DNA-Linked Enzyme-Coupled Assay for Probing Glucosyltransferase Specificity.
ACS Synth. Biol. 4 , 833-41, (2015) Traditional enzyme characterization methods are low-throughput and therefore limit engineering efforts in synthetic biology and biotechnology. Here, we propose a DNA-linked enzyme-coupled assay (DLEnCA) to monitor enzyme reactions in a high-throughput manner.... |
|
|
The combination of plant translational enhancers and terminator increase the expression of human glucocerebrosidase in Nicotiana benthamiana plants.
Plant Sci. 240 , 41-9, (2015) Gaucher's disease is a lysosomal storage disorder caused by mutations in the gene encoding glucocerebrosidase (GCase). It is currently treated by enzyme replacement therapy using recombinant GCase expressed in mammalian cells. Plant production systems are amo... |
|
|
Inhibition of human aldehyde oxidase activity by diet-derived constituents: structural influence, enzyme-ligand interactions, and clinical relevance.
Drug Metab. Dispos. 43(1) , 34-41, (2014) The mechanistic understanding of interactions between diet-derived substances and conventional medications in humans is nascent. Most investigations have examined cytochrome P450-mediated interactions. Interactions mediated by other phase I enzymes are unders... |
|
|
Identification of diet-derived constituents as potent inhibitors of intestinal glucuronidation.
Drug Metab. Dispos. 42(10) , 1675-83, (2014) Drug-metabolizing enzymes within enterocytes constitute a key barrier to xenobiotic entry into the systemic circulation. Furanocoumarins in grapefruit juice are cornerstone examples of diet-derived xenobiotics that perpetrate interactions with drugs via mecha... |
|
|
Antitumor effects of hyaluronan inhibition in desmoid tumors.
Carcinogenesis 36(2) , 272-9, (2015) Desmoid tumors (DTs) are rare, mesenchymal tumors that exhibit features of an abundant wound healing process. Previously, we showed that mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) are constituents of DTs and may contribute to desmoid tumorigenesis via activities associate... |
|
|
Metabolic characterization of meso-dihydroguaiaretic acid in liver microsomes and in mice.
Food Chem. Toxicol. 76 , 94-102, (2015) meso-Dihydroguaiaretic acid (MDGA) is a major component of Myristica fragrans and Machilus thunbergii that is traditionally used as a spice and for medicinal purposes. Despite reports of various biological activities exerted by MDGA, there is no information r... |
|
|
Transporter-mediated uptake of UDP-glucuronic acid by human liver microsomes: assay conditions, kinetics, and inhibition.
Drug Metab. Dispos. 43(1) , 147-53, (2014) This study characterized the kinetics, variability, and factors that affect UDP-glucuronic acid (UDP-GlcUA) uptake by human liver microsomes (HLM). Biphasic kinetics were observed for UDP-GlcUA uptake by HLM. Uptake affinities (assessed as Kd) of the high- an... |
|
|
Phase II metabolism in human skin: skin explants show full coverage for glucuronidation, sulfation, N-acetylation, catechol methylation, and glutathione conjugation.
Drug Metab. Dispos. 43(1) , 126-39, (2014) Although skin is the largest organ of the human body, cutaneous drug metabolism is often overlooked, and existing experimental models are insufficiently validated. This proof-of-concept study investigated phase II biotransformation of 11 test substrates in fr... |