Aceglutamide
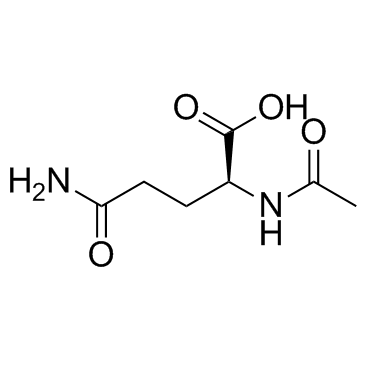
Aceglutamide structure
|
Common Name | Aceglutamide | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 2490-97-3 | Molecular Weight | 188.181 | |
| Density | 1.4±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 419.0±55.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C7H12N2O4 | Melting Point | 206-208 °C | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 207.2±31.5 °C | |
|
Liquid chromatographic-mass spectrometric analysis of N-acetylamino acids in human urine.
J. Chromatogr. B, Biomed. Appl. 657(1) , 15-21, (1994) Liquid chromatography-atmospheric pressure chemical-ionization mass spectrometry (LC-APCI-MS) was used for the analysis of N-acetylamino acids that could not be determined with an amino acid analyzer. LC-APCI-MS could directly detect the protonated molecular ... |
|
|
Availability of glutamine from peptides and acetylglutamine for human tumor-cell cultures.
Metab. Clin. Exp. 38(8 Suppl 1) , 40-2, (1989) In a recent study we showed that the growth behavior of a hematopoietic cell line (K 562) in culture was the same when using glutamine-containing dipeptides or glutamine as substrate. In this article we study the growth behavior of different tumor cells, orig... |
|
|
Understanding carbamoyl-phosphate synthetase I (CPS1) deficiency by using expression studies and structure-based analysis.
Hum. Mutat. 31(7) , 801-8, (2010) Carbamoyl-phosphate synthetase I (CPS1) deficiency (CPS1D), a recessively inherited urea cycle error due to CPS1 gene mutations, causes life-threatening hyperammonemia. The disease-causing potential of missense mutations in CPS1 deficiency can be ascertained ... |
|
|
NMR and MS analysis of decomposition compounds produced from N-acetyl-L-glutamine at low pH.
J. Agric. Food Chem. 48 , 6003-6010, (2000) N-Acetyl-L-glutamine decomposition products glutamine, glutamic acid, pyroglutamic acid, N-acetylglutamic acid, and a novel compound, N-(2,6-dioxo-3-piperidinyl) acetamide, have been identified by NMR and MS techniques. N-Acetylglutamine, a modified amino aci... |
|
|
Absorption of enterally administered N-acetyl-l-glutamine versus glutamine in pigs.
Clin. Nutr. 23 , 1303-1312, (2004) Glutamine instability in liquid media suggests that evaluation of reasonable enteral nutrition sources of glutamine is needed. N-acetyl-l-glutamine offers no instability and no intolerance problems. This research was conducted to study the absorption and appa... |
|
|
N-acetyl-L-glutamine, a liquid-stable source of glutamine, partially prevents changes in body weight and on intestinal immunity induced by protein energy malnutrition in pigs.
Dig. Dis. Sci. 52 , 650-658, (2007) The goal of this study was to evaluate the preventive effect of free glutamine versus N-acetyl-L-glutamine, a liquid-stable source of glutamine, on gut damage induced by protein energy malnutrition in pigs. Healthy pigs (n = 6) were fed a liquid formula for 3... |
|
|
Uptake of doubly-labelled N-acetyl-L-glutamine in rat brain and intestinal mucosa in vivo.
Il Farmaco 36(7) , 347-55, (1981)
|
|
|
N-acetyl functions and acetate detected by nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy of urine to detect renal dysfunction following aminoglycoside and/or glycopeptide antibiotic therapy.
Nephron. Exp. Nephrol. 97(4) , p53-7, (2004) N-acetylneuraminidine (NeuNAc), N-acetylglutamine (GIcNAc) and acetate are metabolites present in normal urine. In patients treated with aminoglycosides and/or glycopeptides, elevation of these metabolites in urine suggests renal tubular injury. NeuNAc, GIcNA... |
|
|
Is alpha-ketoisocaproyl-glutamine a suitable glutamine precursor to sustain fibroblast growth?
Clin. Nutr. 18(1) , 29-33, (1999) Glutamine is considered an essential nutrient for cellular growth.To test the suitability of alpha-ketoisocaproyl-Gln (Kic-Gln) as a new glutamine (Gln) precursor to sustain human fibroblast growth.[3H] thymidine uptake into cellular DNA of human fibroblasts.... |
|
|
New form of pseudohypoparathyroidism with abnormal catalytic adenylate cyclase.
Am. J. Physiol. 257(2 Pt 1) , E277-83, (1989) Patients with pseudohypoparathyroidism type Ia have resistance to multiple hormones because of deficient activity of the stimulatory guanine nucleotide-binding protein (Gs) that couples membrane receptors to activation of adenylate cyclase. However, in a subs... |