Tristealin
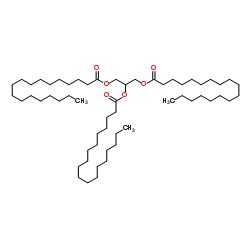
Tristealin structure
|
Common Name | Tristealin | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 555-43-1 | Molecular Weight | 891.480 | |
| Density | 0.9±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 813.0±32.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C57H110O6 | Melting Point | 72-75 °C | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 299.4±25.2 °C | |
|
Fatty acid compositions of triglycerides and free fatty acids in sebum depend on amount of triglycerides, and do not differ in presence or absence of acne vulgaris.
J. Dermatol. 41(12) , 1069-76, (2014) To clarify the influence of the fatty acid composition of sebum in acne vulgaris, we investigated the amounts and fatty acid compositions of triglycerides (TG) and free fatty acids (FFA), and the amounts of cutaneous superficial Propionibacterium acnes in acn... |
|
|
Identification of lipid- and protein-based binders in paintings by direct on-plate wet chemistry and matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization mass spectrometry.
Anal. Bioanal. Chem 407(3) , 1015-22, (2015) Direct on-target plate processing of small (ca. 100 μg) fragments of paint samples for MALDI-MS identification of lipid- and protein-based binders is described. Fragments were fixed on a conventional stainless steel target plate by colloidal graphite followed... |
|
|
Solid lipid nanoparticles-loaded topical gel containing combination drugs: an approach to offset psoriasis.
Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 11(12) , 1833-47, (2014) The primary aim of present work was to develop effective combination drug therapy for topical treatment of psoriasis.Betamethasone dipropionate and calcipotriol loaded solid lipid nanoparticles (CT-BD-SLNs) were prepared by hot melt high shear homogenization ... |
|
|
Development and in vitro characterization of docetaxel-loaded ligand appended solid fat nanoemulsions for potential use in breast cancer therapy.
Artif. Cells. Nanomed. Biotechnol. 43(2) , 93-102, (2015) Breast cancer accounts for 23% of all newly occurring cancers in women worldwide and represents 13.7% of all cancer deaths. Available chemotherapeutic agents are limited largely due to the low accumulation of chemotherapeutics at the tumors relative to their ... |
|
|
Safety studies of post-surgical buprenorphine therapy for mice.
Lab. Anim. 49(2) , 100-10, (2015) The use of appropriate analgesia in laboratory mice may be suboptimal because of concerns about adverse events (AE). Target Animal Safety trials were conducted to determine the safety of an extended-release suspension of buprenorphine. Drug or control suspens... |
|
|
Hard cocoa butter replacers from mango seed fat and palm stearin.
Food Chem. 154 , 323-9, (2014) The blending effects of mango seed fat (MSF), extracted using supercritical fluid, and palm stearin (PS) to formulate hard cocoa butter replacers (CBRs), were investigated. The triglycerides (TG), thermal properties and solid fat content (SFC) of the formulat... |
|
|
Evolution of fat crystal network microstructure followed by NMR.
J. Agric. Food Chem. 59(5) , 1767-73, (2011) Model systems composed of tristearin in solid state and tricaprin in liquid state with different solid-fat content (SFC) and storage time have been investigated by relaxation NMR and NMR diffusometry. The T(2) relaxation of the tricaprin in the melt exhibited... |
|
|
Influence of structural variations on drug release from lipid/polyethylene glycol matrices.
Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 37(5) , 555-62, (2009) Different combinations of monoacid triglycerides and polyethylene glycol powders of different molecular weights were successfully extruded below their melting temperatures as a basis for oral dosage forms. The incorporated polyethylene glycols exhibiting diff... |
|
|
Biodistribution of nanostructured lipid carriers: a tomographic study.
Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 89 , 145-56, (2015) This study describes the preparation, characterization, and biodistribution of radiolabelled nanostructured lipid carriers (NLCs) especially designed for in vivo tomographic study. A preliminary formulative study was conducted in order to incorporate (99m)Tc ... |
|
|
Surfactants have multi-fold effects on skin barrier function.
Eur. J. Dermatol. 25 , 424-35, (2015) The stratum corneum (SC) is responsible for the barrier properties of the skin and the role of intercorneocyte skin lipids, particularly their structural organization, in controlling SC permeability is acknowledged. Upon contacting the skin, surfactants inter... |