2-Oleoyl-1-palmitoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphoethanolamine
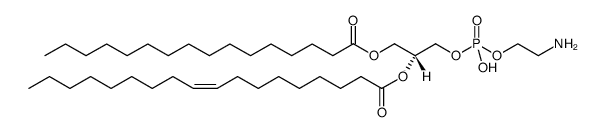
2-Oleoyl-1-palmitoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphoethanolamine structure
|
Common Name | 2-Oleoyl-1-palmitoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphoethanolamine | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 26662-94-2 | Molecular Weight | 717.99600 | |
| Density | N/A | Boiling Point | N/A | |
| Molecular Formula | C39H76NO8P | Melting Point | 24.7 °C (lit.) | |
| MSDS | USA | Flash Point | N/A | |
|
Interactions of a non-fluorescent fluoroquinolone with biological membrane models: A multi-technique approach.
Int. J. Pharm. 495 , 761-70, (2015) Fluoroquinolones are antibiotics which act by penetrating into bacterial cells and inhibiting enzymes related to DNA replication, and metal complexes of these drugs have recently been investigated as one approach to counteracting bacterial resistance. In this... |
|
|
Attractors in Sequence Space: Peptide Morphing by Directed Simulated Evolution.
Mol. Inform. 34 , 709-714, (2016)
|
|
|
Identification of carbonylated lipids from different phospholipid classes by shotgun and LC-MS lipidomics.
Anal. Bioanal. Chem 407 , 5161-73, (2015) Oxidized lipids play a significant role in the pathogenesis of numerous oxidative stress-related human disorders, such as atherosclerosis, obesity, inflammation, and autoimmune diseases. Lipid peroxidation, induced by reactive oxygen and nitrogen species, yie... |
|
|
Potential of novel antimicrobial peptide P3 from bovine erythrocytes and its analogs to disrupt bacterial membranes in vitro and display activity against drug-resistant bacteria in a mouse model.
Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 59 , 2835-41, (2015) With the emergence of many antibiotic-resistant strains worldwide, antimicrobial peptides (AMPs) are being evaluated as promising alternatives to conventional antibiotics. P3, a novel hemoglobin peptide derived from bovine erythrocytes, exhibited modest antim... |
|
|
β2-Microglobulin amyloid fibril-induced membrane disruption is enhanced by endosomal lipids and acidic pH.
PLoS ONE 9(8) , e104492, (2014) Although the molecular mechanisms underlying the pathology of amyloidoses are not well understood, the interaction between amyloid proteins and cell membranes is thought to play a role in several amyloid diseases. Amyloid fibrils of β2-microglobulin (β2m), as... |
|
|
CD300b regulates the phagocytosis of apoptotic cells via phosphatidylserine recognition.
Cell Death Differ. 21(11) , 1746-57, (2014) The CD300 receptor family members are a group of molecules that modulate a variety of immune cell processes. We show that mouse CD300b (CLM7/LMIR5), expressed on myeloid cells, recognizes outer membrane-exposed phosphatidylserine (PS) and does not, as previou... |
|
|
Effect of phospholipid composition on discoidal HDL formation.
Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1828(5) , 1340-6, (2013) Discoidal high-density lipoprotein (HDL) particles are known to fractionalize into several discrete populations. Factors regulating their size are, however, less understood. To reveal the effect of lipid composition on their formation and characteristics, we ... |
|
|
Structures of ABCB10, a human ATP-binding cassette transporter in apo- and nucleotide-bound states.
Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 110(24) , 9710-5, (2013) ABCB10 is one of the three ATP-binding cassette (ABC) transporters found in the inner membrane of mitochondria. In mammals ABCB10 is essential for erythropoiesis, and for protection of mitochondria against oxidative stress. ABCB10 is therefore a potential the... |
|
|
Cholesterol favors the emergence of a long-range autocorrelated fluctuation pattern in voltage-induced ionic currents through lipid bilayers.
Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1828(8) , 1754-64, (2013) The present paper was aimed at evaluating the effect of cholesterol (CHO) on the voltage-induced lipid pore formation in bilayer membranes through a global characterization of the temporal dynamics of the fluctuation pattern of ion currents. The bilayer model... |
|
|
The role of cholesterol on the activity and stability of neurotensin receptor 1.
Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1818(9) , 2228-33, (2012) Understanding the role of specific bilayer components in controlling the function of G-protein coupled receptors (GPCRs) will be a key factor in the development of novel pharmaceuticals. Cholesterol-dependence in particular has become an area of keen interest... |