1,3-BIS-(ALPHA,ALPHA,ALPHA,ALPHAPR,ALPHAPR,ALPHAPR-HEXAFLUORO-3,5-XYLYL)-UREA
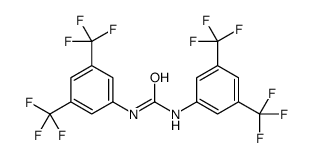
1,3-BIS-(ALPHA,ALPHA,ALPHA,ALPHAPR,ALPHAPR,ALPHAPR-HEXAFLUORO-3,5-XYLYL)-UREA structure
|
Common Name | 1,3-BIS-(ALPHA,ALPHA,ALPHA,ALPHAPR,ALPHAPR,ALPHAPR-HEXAFLUORO-3,5-XYLYL)-UREA | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 3824-74-6 | Molecular Weight | 484.23900 | |
| Density | N/A | Boiling Point | N/A | |
| Molecular Formula | C17H8F12N2O | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | USA | Flash Point | N/A | |
|
Urea derivatives are highly active catalysts for the base-mediated generation of terminal epoxides from aldehydes and trimethylsulfonium iodide.
Org. Biomol. Chem. 6(8) , 1339-43, (2008) N,N'-Diarylureas have been shown to efficiently catalyse sulfonium ylide-mediated aldehyde epoxidation reactions for the first time. These processes are of broad scope and can be coupled with a subsequent Cu(II) ion-catalysed Meinwald rearrangement to give an... |
|
|
Internal Lewis acid assisted hydrogen bond donor catalysis.
Org. Lett. 13(4) , 716-9, (2011) Boronate ureas are introduced as a new class of noncovalent catalysts for conjugate addition reactions with enhanced activity. Through intramolecular coordination of the urea functionality to a strategically placed Lewis acid, rate enhancements up to 10 times... |
|
|
Bonding Organocatalysed Friedel-Crafts Alkylation of Aromatic and Heteroaromatic Systems with Nitroolefins Dessole G,et al.
Synlett 13 , 2374-2378, (2004)
|