Ethyl Oleate
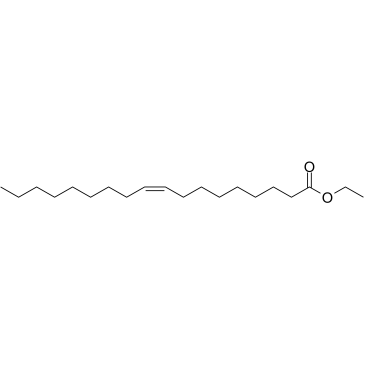
Ethyl Oleate structure
|
Common Name | Ethyl Oleate | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 111-62-6 | Molecular Weight | 310.514 | |
| Density | 0.87 g/mL at 25 °C(lit.) | Boiling Point | 216-218 °C15 mm Hg | |
| Molecular Formula | C20H38O2 | Melting Point | −32 °C(lit.) | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 91.8±20.4 °C | |
|
Fatty acid ethyl esters disrupt neonatal alveolar macrophage mitochondria and derange cellular functioning.
Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 39(3) , 434-44, (2015) Chronic alcohol exposure alters the function of alveolar macrophages (AM), impairing immune defenses in both adult and neonatal lungs. Fatty acid ethyl esters (FAEEs) are biological markers of prenatal alcohol exposure in newborns. FAEEs contribute to alcohol... |
|
|
N-trimethyl chitosan (TMC)-modified microemulsions for improved oral bioavailability of puerarin: preparation and evaluation.
Drug Deliv. 22 , 516-21, (2015) The aim of this research was to increase the oral bioavailability of puerarin by N-trimethyl chitosan-modified microemulsions (TMC-MEs) loaded with puerarin. Different concentrations of TMC-modified microemulsions were prepared in our study, and then evaluate... |
|
|
Transcutaneous delivery of leflunomide nanoemulgel: Mechanistic investigation into physicomechanical characteristics, in vitro anti-psoriatic and anti-melanoma activity.
Int. J. Pharm. 487 , 148-56, (2015) The present study is a mechanistic validation of 'proof of concept' of effective topical delivery of leflunomide (LFD) nanoemulgel for localized efficient treatment of psoriatic lesions as well as melanoma affected skin regions. Hyperproliferation of keratino... |
|
|
Optimized mixed oils remarkably reduce the amount of surfactants in microemulsions without affecting oral bioavailability of ibuprofen by simultaneously enlarging microemulsion areas and enhancing drug solubility.
Int. J. Pharm. 487 , 17-24, (2015) The toxicity and irritation associated with high amounts of surfactants restrict the extensive utilization of microemulsions. To address these shortcomings, employing mixed oils to enlarge microemulsion areas therefore reducing surfactant contents is a promis... |
|
|
Preparation, characterization, and preliminary antibrowning evaluations of norartocarpetin microemulsions.
J. Agric. Food Chem. 63(5) , 1615-21, (2015) Norartocarpetin is a flavone widely distributed in Moraceae plants with strong tyrosinase inhibitory activity. However, its poor solubility in aqueous systems and in food grade solvents (oils) limits its extensive applications. The aim of this study was to im... |
|
|
Optimization, ex vivo permeation, and stability study of lipid nanocarrier loaded gelatin capsules for treatment of intermittent claudication.
Int. J. Nanomedicine 10 , 4459-78, (2015) In this study, an optimized nanodispersible oral dosage form (containing a lactate ester) was developed for cilostazol (CZL). CZL is a phosphodiesterase inhibitor used for intermittent claudication. We aimed to improve the dissolution rate and absorption of C... |
|
|
A comparative study of biodiesel production using methanol, ethanol, and tert-butyl methyl ether (MTBE) under supercritical conditions.
Bioresour. Technol. 191 , 306-11, (2015) In this study, biodiesel production under supercritical conditions among methanol, ethanol, and tert-butyl methyl ether (MTBE) was compared in order to elucidate the differences in their reaction behavior. A continuous reactor was employed, and experiments we... |
|
|
Preparation, characterization, sterility validation, and in vitro cell toxicity studies of microemulsions possessing potential parenteral applications.
Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 39(2) , 240-51, (2013) Water-in-oil microemulsions (w/o ME) are ideal for parenteral drug delivery. However, no such formulations have been tested for biocompatibility in in vitro cell cultures. Furthermore, sterilization of w/o MEs is a challenging process that has not been previo... |
|
|
QbD-Oriented Development of Self-Nanoemulsifying Drug Delivery Systems (SNEDDS) of Valsartan with Improved Biopharmaceutical Performance.
Curr. Drug Deliv. 12 , 544-63, (2015) The objectives of the present studies were to develop the systematically optimized selfnanoemulsifying drug delivery systems (SNEDDS) of valsartan employing the holistic QbD approach. The quality profile target product (QTPP) was defined and critical quality ... |
|
|
Effect of lipolysis on drug release from self-microemulsifying drug delivery systems (SMEDDS) with different core/shell drug location.
AAPS PharmSciTech 15(3) , 731-40, (2014) The objective of this study is to investigate the effect of lipolysis on the release of poorly water-soluble drug from SMEDDS in the perspective of drug core/shell location. For this purpose, four SMEDDS formulations with various core/shell properties were de... |