| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
Glycerol
CAS:56-81-5 |
|
 |
Ethanol
CAS:64-17-5 |
|
 |
DL-Methionine
CAS:59-51-8 |
|
 |
HEPES
CAS:7365-45-9 |
|
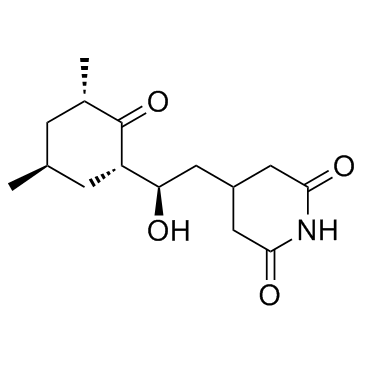 |
Cycloheximide
CAS:66-81-9 |
|
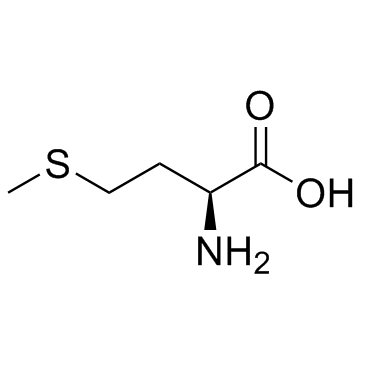 |
L-Methionine
CAS:63-68-3 |