Cycloheximide
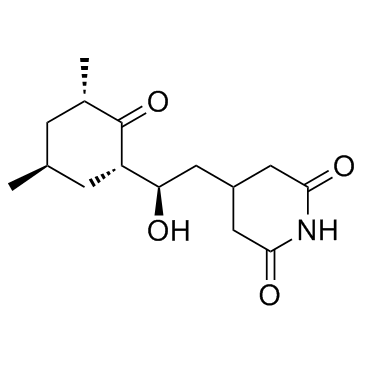
Cycloheximide structure
|
Common Name | Cycloheximide | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 66-81-9 | Molecular Weight | 281.347 | |
| Density | 1.1±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 491.8±10.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C15H23NO4 | Melting Point | 111-116 °C | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 251.2±19.0 °C | |
| Symbol |



GHS06, GHS08, GHS09 |
Signal Word | Danger | |
Use of CycloheximideCycloheximide (Naramycin A) is an eukaryote protein synthesis inhibitor, with IC50s of 532.5 nM and 2880 nM for protein synthesis and RNA synthesis in vivo, respectively. |
| Name | cicloheximide |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Cycloheximide (Naramycin A) is an eukaryote protein synthesis inhibitor, with IC50s of 532.5 nM and 2880 nM for protein synthesis and RNA synthesis in vivo, respectively. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
IC50: 532.5 nM (protein synthesis), 2.88 μM (RNA synthesis)[1] |
| In Vitro | Cycloheximide (CHX) is the most common laboratory reagent used to inhibit protein synthesis. Cycloheximide has been shown to block the elongation phase of eukaryotic translation. Cycloheximide binds the ribosome and inhibits eEF2-mediated translocation. Surprisingly, Cycloheximide allows one complete translocation cycle to proceed before halting any further elongation. Cycloheximide has been speculated that Cycloheximide requires an E-site bound deacylated tRNA for activity[1]. |
| In Vivo | The mice receive Cycloheximide injections at 30, 60, or 120 mg/kg prior to training with a 200 µA shock. There is a significant effect of Cycloheximide on latencies on the memory test trials (P<0.001). In saline controls, this shock level results in latencies on the test trial that are significantly higher than those at training. Injections of the lowest dose of Cycloheximide tested, 30 mg/kg, results in latencies on the test trial that are significantly higher than those seen in the saline control group. Mice receiving either of the two higher doses of Cycloheximide has latencies on the test trial that are comparable to those of the saline group, i.e., the higher doses neither enhanced nor impaired memory under these conditions, resulting in an inverted-U dose-response curve for Cycloheximide enhancement of memory[2]. Infarct volume, as measured by morphometric analysis of infarct areas with triphenyl tetrazolium chloride (TTC), is significantly reduced by 92% and 61% when Cycloheximide is given 0 or 6 hr after HI respectively, but shows an insignificant trend in infarct reduction if Cycloheximide is administered 12 hr after hypoxia-ischemia (HI) compared to the HI control group, and no protective effect is observed when administration is delayed until 24 hr after HI[3]. |
| Cell Assay | To test cell proliferation, 3000-5000 cells (HeLa, HTB1 and HEK 293T cells; Jurkat, BT 474, HCC 1395, HCC 1937, HCC 2218 and MDA MB231 cells; MCF 10A) per well are plated in a 96-well plate and allowed to adhere overnight. Cycloheximide dissolved in DMSO at the indicated concentrations (0.1 nM-1000μM) are then added and cells are incubated for a further 24 h. [3H]-thymidine is added at 1 μCi per well and incubation is continued for an additional 7 h. Cells are washed twice with PBS and then trypsinized before they are collected with a Tomtec harvester and bound to GF/C filter mats. Thymidine uptake is then measured by scintillation counting[1]. |
| Animal Admin | Mice[2] Male ICR mice (approximately 2 months old) are used in this experiment. Cycloheximide is administered IP at concentrations of 0 (saline controls), 30, 60, or 120 mg/kg. Cycloheximide injections are administered 30 min prior to training. The 120 mg/kg dose is commonly used to study amnesia in mice. Note that amnestic Cycloheximide doses are much lower in rats (1-3 mg/kg) than in mice, consistent with a similar difference in LD50s for rats and mice. Cycloheximide doses of 120-150 mg/kg result in approximately 95% inhibition of brain protein synthesis as measured 30-60 min after injection; the dose of 30 mg/kg produces approximately 80% inhibition of brain protein synthesis. Rats[3] Unilateral carotid artery ligation is performed in 7-day old Sprague Dawley rat pups under methoxyflurane anesthesia. The neck is incised in the midline, and the right common carotid artery is permanently ligated with 4-0 silk. Total time of surgery in each animal never exceeded 5 min. Following surgery, rats are returned to their mother for recovery and feeding for 2 hr. The pups are then exposed to a 100 min-period of hypoxia (8% O2, 92% N2) by placing them in an airtight chamber partially submerged in a temperature controlled water bath to maintain the ambient temperature inside the chamber at a constant 36°C. In the HI with Cycloheximide treatment group, the rat pups receive an intraperitoneal injection of Cycloheximide at a dose of 0.6 mg/kg at 0, 6, 12 or 24 hr of recovery, and an equal volume of normal saline is given to a HI control group. Then, the rat pups are returned to their dam until sacrifice; the whole brain tissue is obtained under deep pentobarbital anesthesia (60 mg/kg, intraperitoneal) for flow cytometry and triphenyl tetrazolium chloride (TTC) at 48 and 72 hr after HI, respectively. |
| References |
| Density | 1.1±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 491.8±10.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 111-116 °C |
| Molecular Formula | C15H23NO4 |
| Molecular Weight | 281.347 |
| Flash Point | 251.2±19.0 °C |
| Exact Mass | 281.162720 |
| PSA | 83.47000 |
| LogP | 0.56 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±2.8 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.499 |
| InChIKey | YPHMISFOHDHNIV-FSZOTQKASA-N |
| SMILES | CC1CC(C)C(=O)C(C(O)CC2CC(=O)NC(=O)C2)C1 |
| Water Solubility | 2.1 g/100 mL (2 ºC) |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
MUTATION DATA
|
| Symbol |



GHS06, GHS08, GHS09 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Danger |
| Hazard Statements | H300-H341-H360D-H411 |
| Precautionary Statements | Missing Phrase - N15.00950417-P201-P280-P308 + P313 |
| Personal Protective Equipment | Eyeshields;Faceshields;full-face respirator (US);Gloves;multi-purpose combination respirator cartridge (US);type ABEK (EN14387) respirator filter |
| Hazard Codes | T+:Verytoxic;N:Dangerous for the environment; |
| Risk Phrases | R28;R51/53;R61;R68 |
| Safety Phrases | S53-S45-S61 |
| RIDADR | UN 2811 6.1/PG 1 |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
| RTECS | MA4375000 |
| Packaging Group | II |
| Hazard Class | 6.1(a) |
| HS Code | 29419000 |
|
~% 
Cycloheximide CAS#:66-81-9
Detail
|
| Literature: Agricultural and Biological Chemistry, , vol. 48, # 9 p. 2315 - 2319 |
|
~% 
Cycloheximide CAS#:66-81-9 |
| Literature: Agricultural and Biological Chemistry, , vol. 48, # 9 p. 2315 - 2319 |

Cycloheximide CAS#:66-81-9 ~% 
Cycloheximide CAS#:66-81-9 |
| Literature: Agricultural and Biological Chemistry, , vol. 48, # 9 p. 2315 - 2319 |
| HS Code | 29419000 |
|---|
|
A survey of the interactome of Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus ORF45 revealed its binding to viral ORF33 and cellular USP7, resulting in stabilization of ORF33 that is required for production of progeny viruses.
J. Virol. 89(9) , 4918-31, (2015) The ORF45 protein of Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus (KSHV) is a gammaherpesvirus-specific immediate-early tegument protein. Our previous studies have revealed its crucial roles in both early ... |
|
|
Inducible, tightly regulated and growth condition-independent transcription factor in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.
Nucleic Acids Res. 42(17) , e130, (2014) The precise control of gene expression is essential in basic biological research as well as in biotechnological applications. Most regulated systems available in yeast enable only the overexpression o... |
|
|
Endoplasmic reticulum stress sensitizes cells to DNA damage-induced apoptosis through p53-dependent suppression of p21(CDKN1A).
Nat. Commun. 5 , 5067, (2014) Endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress occurs in poorly perfused tissues and activates the p53 isoform p53/47 to promote G2 arrest via 14-3-3σ. This contrasts with the p21(CDKN1A)-dependent G1 arrest cause... |
| 4-[2-(3,5-dimethyl-2-oxocyclohexyl)-2-hydroxyethyl]glutarimide |
| 4-{(2R)-2-[(1S,3S,5S)-3,5-dimethyl-2-oxocyclohexyl]-2-hydroxyethyl}piperidine-2,6-dione |
| Acti-Aid |
| Actidion |
| ACTIDIONE |
| NARAMYCIN A |
| Actidone |
| cyclohexamide |
| MFCD06202064 |
| Hizarocin |
| cycloheximide |
| Kaken |
| 4-[(2R)-2-[(1S,3S,5S)-3,5-dimethyl-2-oxocyclohexyl]-2-hydroxyethyl]-2,6-piperidinedione |
| EINECS 200-636-0 |
| Cicloheximide |
| 4-[(2R)-2-[(1S,3S,5S)-3,5-dimethyl-2-oxocyclohexyl]-2-hydroxyethyl]piperidine-2,6-dione |


![[1-(3,5-dimethyl-2-oxo-cyclohexyl)-2-(2,6-dioxo-4-piperidyl)ethyl] acetate structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/117/1508-62-9.png) CAS#:1508-62-9
CAS#:1508-62-9![2,6-Piperidinedione, 4-[2- (2-hydroxy-3,5-dimethylphenyl)-2-oxoethyl]- structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/396/526-02-3.png) CAS#:526-02-3
CAS#:526-02-3