| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
Glycerol
CAS:56-81-5 |
|
 |
sucrose
CAS:57-50-1 |
|
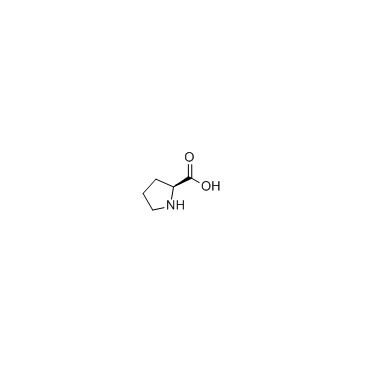 |
Proline
CAS:147-85-3 |
|
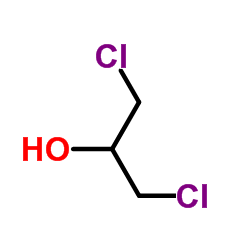 |
1,3-Dichloro-2-propanol
CAS:96-23-1 |
|
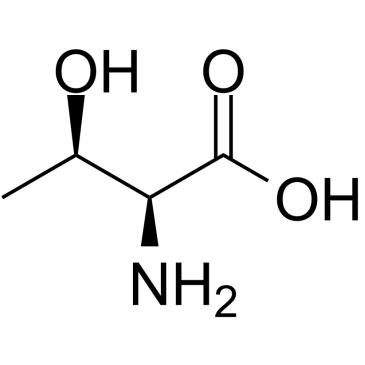 |
L-Threonine
CAS:72-19-5 |
|
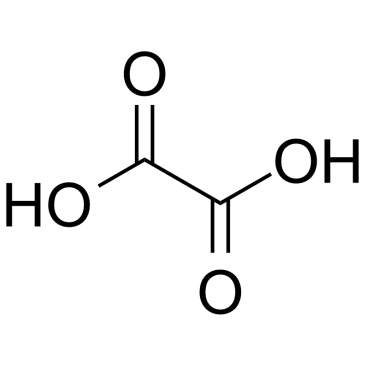 |
Oxalic acid
CAS:144-62-7 |
|
 |
Styrene
CAS:100-42-5 |
|
 |
Glycidol
CAS:556-52-5 |
|
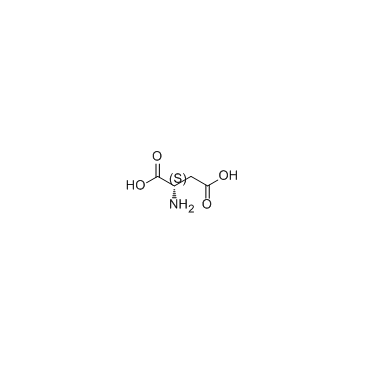 |
L-Aspartic acid
CAS:56-84-8 |
|
 |
DL-Phenylalanine
CAS:150-30-1 |