1,3-Dichloro-2-propanol
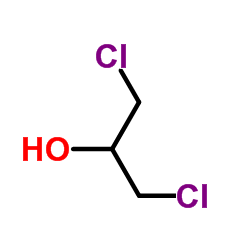
1,3-Dichloro-2-propanol structure
|
Common Name | 1,3-Dichloro-2-propanol | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 96-23-1 | Molecular Weight | 128.985 | |
| Density | 1.3±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 174.3±0.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C3H6Cl2O | Melting Point | -4 °C | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 85.6±0.0 °C | |
| Symbol |


GHS06, GHS08 |
Signal Word | Danger | |
| Name | 1,3-dichloropropan-2-ol |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Density | 1.3±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 174.3±0.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | -4 °C |
| Molecular Formula | C3H6Cl2O |
| Molecular Weight | 128.985 |
| Flash Point | 85.6±0.0 °C |
| Exact Mass | 127.979568 |
| PSA | 20.23000 |
| LogP | 0.66 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.4±0.7 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.462 |
| InChIKey | DEWLEGDTCGBNGU-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| SMILES | OC(CCl)CCl |
| Water Solubility | soluble. >=10 g/100 mL at 23 ºC |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
MUTATION DATA
|
| Symbol |


GHS06, GHS08 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Danger |
| Hazard Statements | H301-H312-H350 |
| Precautionary Statements | P201-P280-P301 + P310-P308 + P313 |
| Personal Protective Equipment | Eyeshields;Faceshields;full-face respirator (US);Gloves;multi-purpose combination respirator cartridge (US);type ABEK (EN14387) respirator filter |
| Hazard Codes | T:Toxic; |
| Risk Phrases | R21;R25;R45 |
| Safety Phrases | S53-S45-S36/37-S16 |
| RIDADR | UN 2750 6.1/PG 2 |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
| RTECS | UB1400000 |
| Packaging Group | II |
| Hazard Class | 6.1 |
| HS Code | 29055910 |
| Precursor 10 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 10 | |
| HS Code | 2905590090 |
|---|---|
| Summary | 2905590090 other halogenated, sulphonated, nitrated or nitrosated derivatives of acyclic alcohols。Supervision conditions:None。VAT:17.0%。Tax rebate rate:9.0%。MFN tariff:5.5%。General tariff:30.0% |
|
Mechanism of chemical activation of sodium chloride in the presence of amino acids.
Food Chem. 166 , 301-8, (2014) Sodium chloride has been shown to promote chlorination of glycerol during thermal processing. However, the detailed mechanism of this reaction is not well understood. Preliminary experiments have indi... |
|
|
Exploring the enantioselective mechanism of halohydrin dehalogenase from Agrobacterium radiobacter AD1 by iterative saturation mutagenesis.
Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 81(8) , 2919-26, (2015) Halohydrin dehalogenase from Agrobacterium radiobacter AD1 (HheC) shows great potential in producing valuable chiral epoxides and β-substituted alcohols. The wild-type (WT) enzyme displays a high R-en... |
|
|
Halogenated derivatives QSAR model using spectral moments to predict haloacetic acids (HAA) mutagenicity.
Bioorg. Med. Chem. 16 , 5720-32, (2008) The risk of the presence of haloacetic acids in drinking water as chlorination by-products and the shortage of experimental mutagenicity data for most of them requires a research work. This paper desc... |
| 1,3-dichloro-1,3-dideoxyglycerol |
| 2-Propanol, 1,3-dichloro- |
| glycerol 1,3-dichlorohydrin |
| U 25,354 |
| 1,3-dichloro-2-hydroxypropane |
| EINECS 202-491-9 |
| 1,3-dichlorohydrin |
| DCP |
| gdch |
| 1,3-DCP |
| Enodrin |
| 1,3-di-chloro-2-propanol |
| 1,3-dichloro-2-propyl alcohol |
| Dichlorohydrin |
| 1,3-dichloropropan-2-ol |
| MFCD00000951 |
| 1,3-Dichloro-2-propanol |
| Glycerol-α,γ-dichlorohydrin |
 CAS#:56-81-5
CAS#:56-81-5 CAS#:106-89-8
CAS#:106-89-8 CAS#:107-05-1
CAS#:107-05-1 CAS#:96-24-2
CAS#:96-24-2 CAS#:64-19-7
CAS#:64-19-7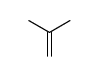 CAS#:115-11-7
CAS#:115-11-7 CAS#:534-07-6
CAS#:534-07-6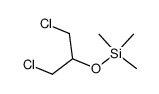 CAS#:7453-13-6
CAS#:7453-13-6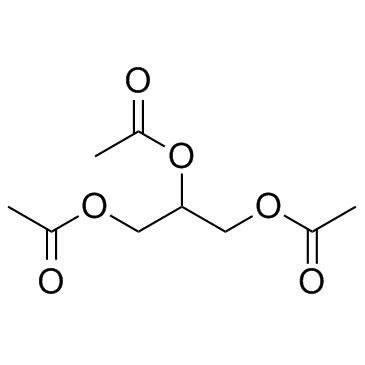 CAS#:102-76-1
CAS#:102-76-1 CAS#:693-03-8
CAS#:693-03-8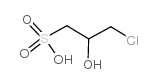 CAS#:107-57-3
CAS#:107-57-3 CAS#:10304-16-2
CAS#:10304-16-2 CAS#:542-75-6
CAS#:542-75-6 CAS#:555-43-1
CAS#:555-43-1 CAS#:921-03-9
CAS#:921-03-9 CAS#:14569-62-1
CAS#:14569-62-1 CAS#:67843-74-7
CAS#:67843-74-7 CAS#:51594-55-9
CAS#:51594-55-9 CAS#:513-88-2
CAS#:513-88-2
