| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
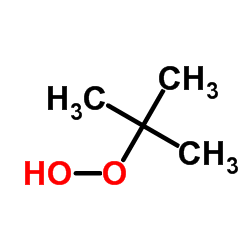 |
tert-Butyl Hydroperoxide
CAS:75-91-2 |
|
 |
α-Synuclein (61-95) (human) trifluoroacetate salt
CAS:154040-19-4 |
|
 |
Acetylcysteine(N-acetylcysteine)
CAS:616-91-1 |
|
 |
Glutathione
CAS:70-18-8 |