Acetylcysteine(N-acetylcysteine)

Acetylcysteine(N-acetylcysteine) structure
|
Common Name | Acetylcysteine(N-acetylcysteine) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 616-91-1 | Molecular Weight | 163.195 | |
| Density | 1.3±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 407.7±40.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C5H9NO3S | Melting Point | 106-108 °C(lit.) | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 200.4±27.3 °C | |
Use of Acetylcysteine(N-acetylcysteine)Acetylcysteine is a mucolytic agent which reduces the thickness of the mucus. |
| Name | N-acetyl-L-cysteine |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Acetylcysteine is a mucolytic agent which reduces the thickness of the mucus. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
Human Endogenous Metabolite |
| In Vitro | N-acetylcysteine prevents apoptotic DNA fragmentation and maintains long-term survival in the absence of other trophic support in serum-deprived PC12 cells. N-acetylcysteine also prevents death of PC12 cells and sympathetic neurons[2]. N-acetylcysteine causes dose-dependent reductions in viability in rat and human aortic smooth muscle cells[3]. N-acetylcysteine activates the Ras-extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) pathway in PC12 cells. N-acetylcysteine protects neuronal cells from death evoked by withdrawal of trophic support. N-acetylcysteine increases nitric oxide (NO) release from protein-bound stores in vascular tissue. N-acetylcysteine pretreatment of PC12 cells interferes with NGF-dependent signaling and neurite outgrowth, and it is suggested that N-acetylcysteine interferes with redox-sensitive steps in the NGF mechanism[4]. |
| In Vivo | N-acetylcysteine (150, 300 mg/kg) treatment significantly reduces liver transaminases in all groups of treatment, mostly in group N-acetylcysteine 300. Lung glutathione peroxidase is significantly increases in group N-acetylcysteine 300 (P=0.04), while the other oxidation biomarkers show no significant differences[1]. N-acetylcysteine improves cognition of 12-month-old SAMP8 mice in both the T-maze footshock avoidance paradigm and the lever press appetitive task without inducing non-specific effects on motor activity, motivation to avoid shock, or body weight[5]. |
| Cell Assay | For survival experiments, washed cells are resuspended in RPM1 1640 medium and plated in 0.5 mL at a density of 8-10×105 per well in 24 well plastic culture dishes coated with rat tail collagen. To feed, but to avoid loss of floating cells, fresh medium (0.2 mL) is added to the cultures on days 1, 5, and 10. For experiments involving "primed" PC12 cells, cultures are pretreated for l-2 weeks with NGF in RPM1 1640 medium supplemented with 1% heat-iN-acetylcysteinetivated horse serum. The cells are then washed and passaged into serum-free RPM1 1640 medium. |
| Animal Admin | Rats: Rats are randomLy allocated into five groups: sham group (n=5), control group with IIR (n=8) and three groups with IIR who are given N-acetylcysteine in different dosages: 150 mg/kg intraperitoneally 5 min before ischemia (n=8, group N-acetylcysteine 150), 300 mg/kg i.p 5 min before ischemia (n=7, group N-acetylcysteine 300), and 150 mg/kg i.p 5 min before ischemia plus 150 mg/kg 5 min before reperfusion (n=7, group N-acetylcysteine 150 + 150). After 4 h of reperfusion, the animals are euthanized by exsanguination from the abdominal aorta. |
| References |
| Density | 1.3±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 407.7±40.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 106-108 °C(lit.) |
| Molecular Formula | C5H9NO3S |
| Molecular Weight | 163.195 |
| Flash Point | 200.4±27.3 °C |
| Exact Mass | 163.030319 |
| PSA | 105.20000 |
| LogP | -0.15 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±2.0 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.519 |
| InChIKey | PWKSKIMOESPYIA-BYPYZUCNSA-N |
| SMILES | CC(=O)NC(CS)C(=O)O |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
|
| Personal Protective Equipment | Eyeshields;Gloves;type N95 (US);type P1 (EN143) respirator filter |
|---|---|
| Risk Phrases | R36/37/38 |
| Safety Phrases | S22-S24/25 |
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
| RTECS | HA1660000 |
| HS Code | 2930909090 |
|
~% 
Acetylcysteine(... CAS#:616-91-1 |
| Literature: Journal of Antibiotics, , vol. 63, # 2 p. 95 - 96 |
|
~% 
Acetylcysteine(... CAS#:616-91-1 |
| Literature: Biochemical Journal, , vol. 25, p. 619 Biochemical Journal, , vol. 27, p. 1716 |
|
~% 
Acetylcysteine(... CAS#:616-91-1 |
| Literature: Journal of medicinal chemistry, , vol. 11, # 6 p. 1176 - 1182 |
|
~% 
Acetylcysteine(... CAS#:616-91-1 |
| Literature: Biochemical Journal, , vol. 25, p. 619 Biochemical Journal, , vol. 27, p. 1716 |
|
~% 
Acetylcysteine(... CAS#:616-91-1 |
| Literature: Liebigs Annalen der Chemie, , # 1 p. 22 - 33 |
| Precursor 6 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 8 | |
| HS Code | 2930909090 |
|---|---|
| Summary | 2930909090. other organo-sulphur compounds. VAT:17.0%. Tax rebate rate:13.0%. . MFN tariff:6.5%. General tariff:30.0% |
|
Ellipticine induces apoptosis in T-cell lymphoma via oxidative DNA damage.
Leuk. Lymphoma 56(3) , 739-47, (2015) The tumor suppressor p53 is often mutated in human cancers. Restoring its antitumor activity has been shown to be a promising therapeutic approach for cancer treatment. Here we analyzed the activity a... |
|
|
Mitochondrial dynamics regulate melanogenesis through proteasomal degradation of MITF via ROS-ERK activation.
Pigment Cell Melanoma Res. 27(6) , 1051-62, (2014) Mitochondrial dynamics control mitochondrial functions as well as their morphology. However, the role of mitochondrial dynamics in melanogenesis is largely unknown. Here, we show that mitochondrial dy... |
|
|
Antiviral effect of methylated flavonol isorhamnetin against influenza.
PLoS ONE 10(3) , e0121610, (2015) Influenza is an infectious respiratory disease with frequent seasonal epidemics that causes a high rate of mortality and morbidity in humans, poultry, and animals. Influenza is a serious economic conc... |
| AC-ASP-GLU |
| 2-(acetylamino)-3-sulfanylpropanoic acid |
| N-acetyl-L-aspartyl-L-glutamate |
| Acetylcysteine |
| (R)-2-Acetamido-3-mercaptopropanoic acid |
| AC-ASP-GLU H2O |
| MFCD00004880 |
| N-Acetylcysteine |
| EINECS 210-498-3 |
| N-acetyl-aspartatylglutamate |
| NAAGA |
| SPAGLUMIC ACID |
| N-acetylcycteine |
| N-ACETYL-3-MERCAPTOALANINE |
| AC-ASP-GLU-OH |
| L-N-acetyl-cysteine |
| Isospaglumic acid |
| (2R)-2-acetylamino-2-carboxyethanethiol |
| N-acetyl-L-aspartyl-L-glutamic acid |
| Cysteine, N-acetyl- |
| N-acetyl-(R)-cysteine |
| Naaxia |
| ACETYL-D-E |
| N-Acetyl-L-Cysteine |
| NAAG |
| N-Acetyl-cysteine |




 CAS#:56-88-2
CAS#:56-88-2 CAS#:2998-83-6
CAS#:2998-83-6 CAS#:5545-17-5
CAS#:5545-17-5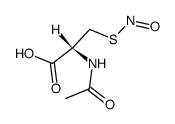 CAS#:56577-02-7
CAS#:56577-02-7![trans-[Pt(OH)2(c-C6H11NH2)(NH3)] structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/455/1034767-14-0.png) CAS#:1034767-14-0
CAS#:1034767-14-0 CAS#:35897-25-7
CAS#:35897-25-7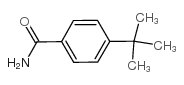 CAS#:56108-12-4
CAS#:56108-12-4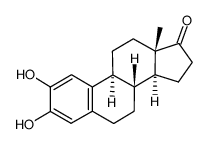 CAS#:362-06-1
CAS#:362-06-1
