| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
Sulfuric acid
CAS:7664-93-9 |
|
 |
Acetone
CAS:67-64-1 |
|
 |
Hydrochloric acid
CAS:7647-01-0 |
|
 |
sucrose
CAS:57-50-1 |
|
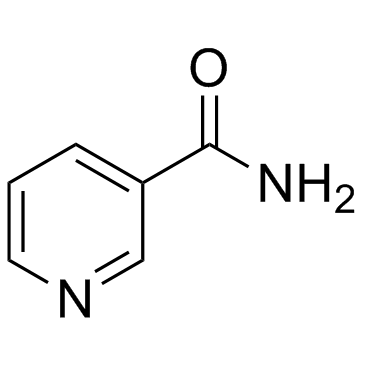 |
Nicotinamide
CAS:98-92-0 |
|
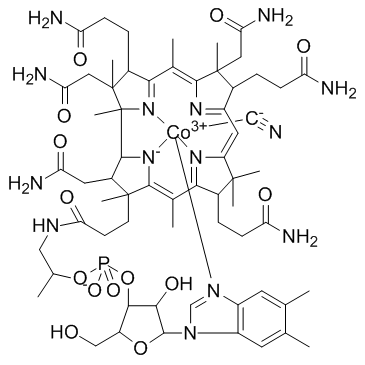 |
Vitamin B12
CAS:68-19-9 |
|
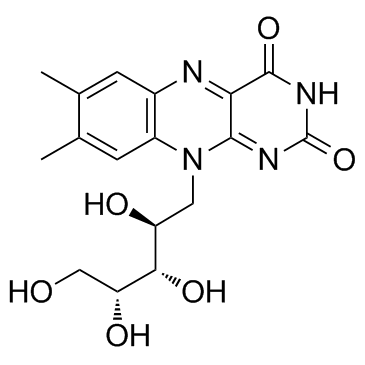 |
Riboflavine
CAS:83-88-5 |
|
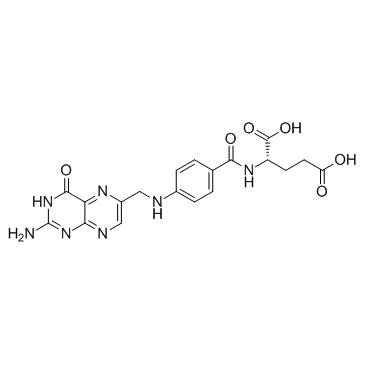 |
Folic Acid
CAS:59-30-3 |
|
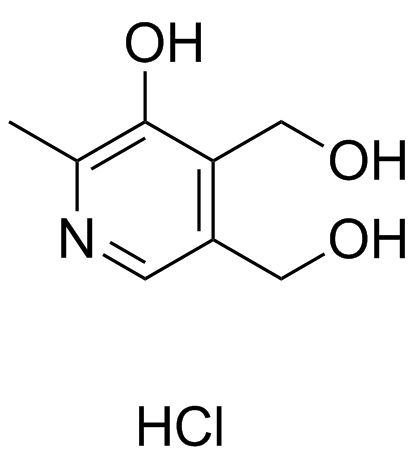 |
Pyridoxine hydrochloride
CAS:58-56-0 |
|
 |
Calcium pantothenate
CAS:137-08-6 |