| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
Ethidium bromide
CAS:1239-45-8 |
|
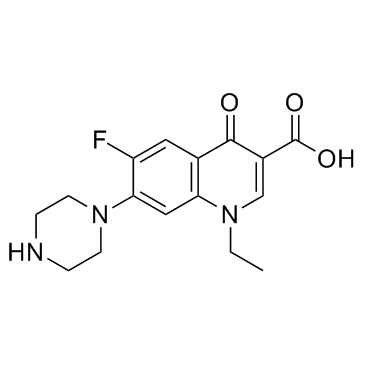 |
Norfloxacin
CAS:70458-96-7 |
|
 |
Nalidixic acid
CAS:389-08-2 |
|
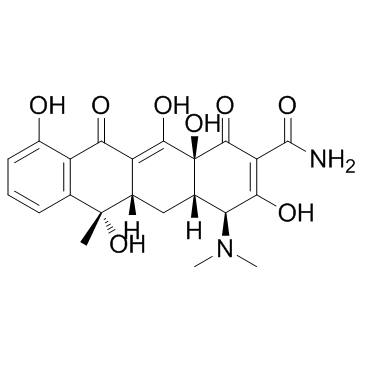 |
Tetracycline
CAS:60-54-8 |
|
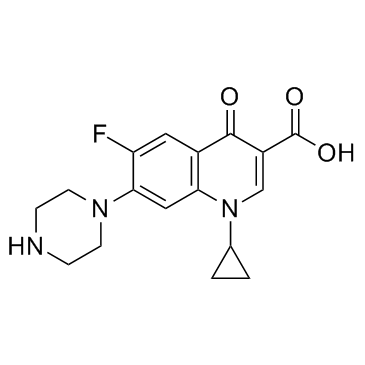 |
Ciprofloxacin
CAS:85721-33-1 |
|
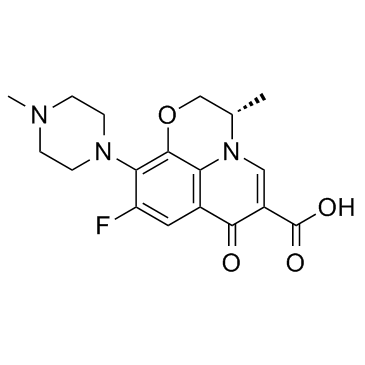 |
Levofloxacin
CAS:100986-85-4 |
|
 |
Ampicillin
CAS:69-53-4 |