| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
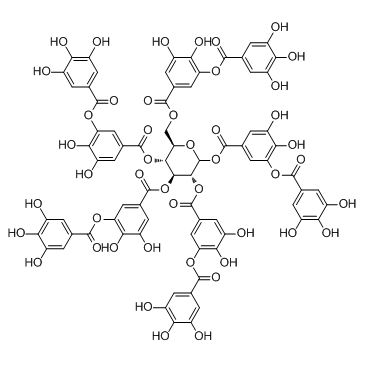 |
Tannic acid
CAS:1401-55-4 |
|
 |
Pyrogallol
CAS:87-66-1 |
|
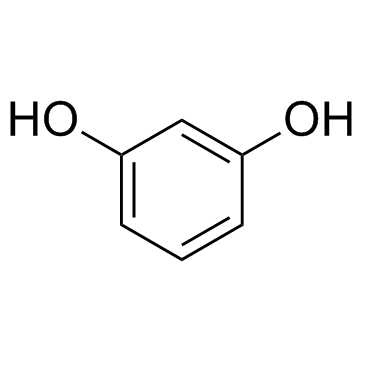 |
Resorcine
CAS:108-46-3 |
|
 |
Salicylic acid
CAS:69-72-7 |
|
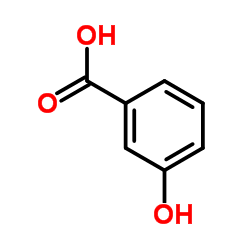 |
3-Hydroxybenzoicacid
CAS:99-06-9 |
|
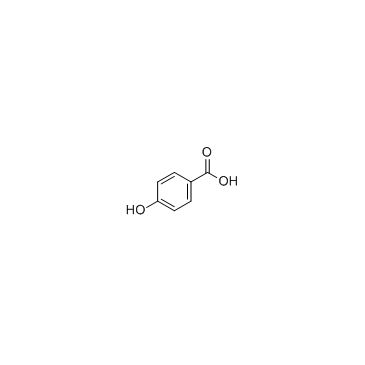 |
4-Hydroxybenzoic acid
CAS:99-96-7 |
|
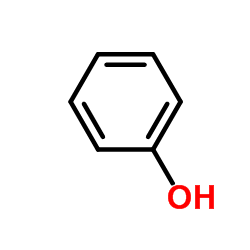 |
Phenol
CAS:108-95-2 |
|
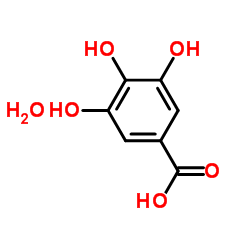 |
Gallic acid hydrate
CAS:5995-86-8 |
|
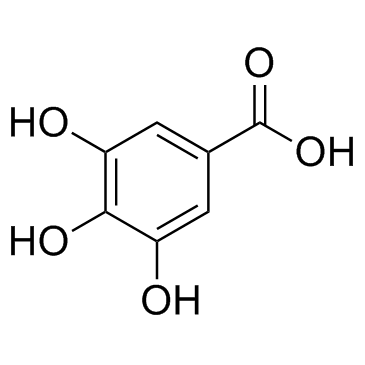 |
Gallic acid
CAS:149-91-7 |
|
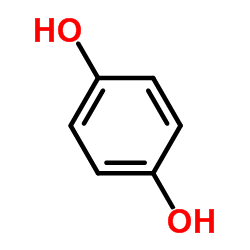 |
Hydroquinone
CAS:123-31-9 |