| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
1-(3-Dimethylaminopropyl)-3-ethylcarbodiimide hydrochloride
CAS:25952-53-8 |
|
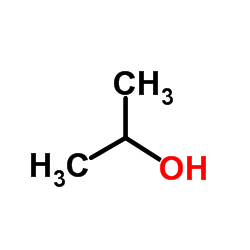 |
Isopropanol
CAS:67-63-0 |
|
 |
Ethanol
CAS:64-17-5 |
|
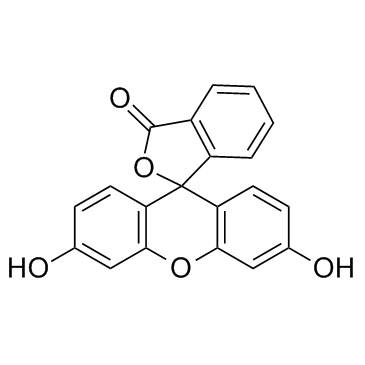 |
Fluorescein
CAS:2321-07-5 |
|
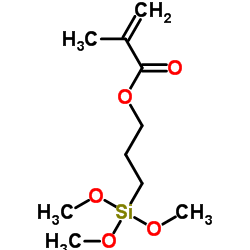 |
3-Methacryloxypropyltrimethoxysilane
CAS:2530-85-0 |
|
 |
L-Glutamine
CAS:56-85-9 |
|
 |
acetic acid
CAS:64-19-7 |
|
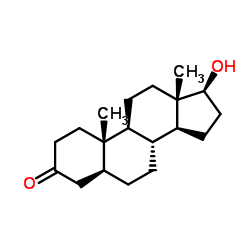 |
Stanolone
CAS:521-18-6 |
|
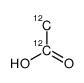 |
acetic acid
CAS:1173022-32-6 |
|
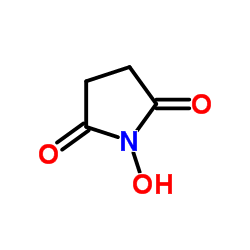 |
N-Hydroxysuccinimide
CAS:6066-82-6 |