| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
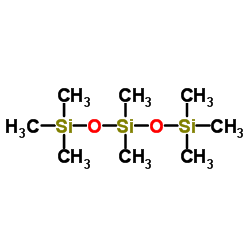 |
Octamethyltrisiloxane
CAS:107-51-7 |
|
 |
Hexamethyldisiloxane
CAS:107-46-0 |
|
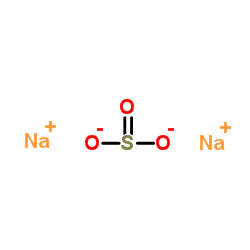 |
Sodium sulfite
CAS:7757-83-7 |
|
 |
Methanol
CAS:67-56-1 |
|
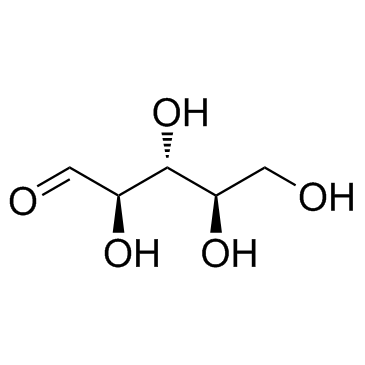 |
D-Ribose
CAS:50-69-1 |
|
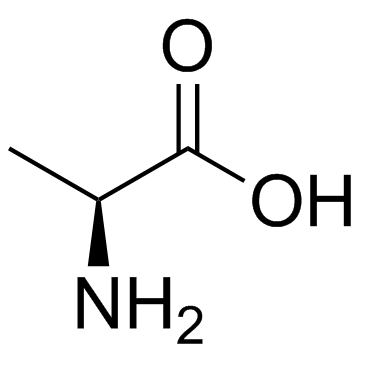 |
L-alanine
CAS:56-41-7 |
|
 |
magnesium sulfate
CAS:7487-88-9 |
|
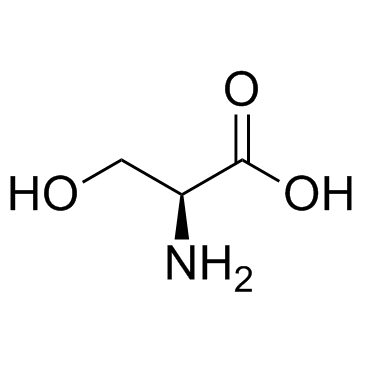 |
L-serine
CAS:56-45-1 |
|
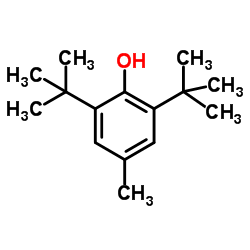 |
Butylated hydroxytoluene
CAS:128-37-0 |
|
 |
Furan
CAS:110-00-9 |