L-alanine
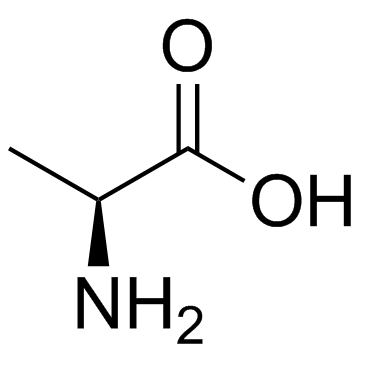
L-alanine structure
|
Common Name | L-alanine | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 56-41-7 | Molecular Weight | 89.093 | |
| Density | 1.2±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 212.9±23.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C3H7NO2 | Melting Point | 314.5 °C (dec.)(lit.) | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 82.6±22.6 °C | |
Use of L-alanineL-Alanine is a non-essential amino acid, involved in sugar and acid metabolism, increases immunity, and provides energy for muscle tissue, brain, and central nervous system. |
| Name | L-alanine |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | L-Alanine is a non-essential amino acid, involved in sugar and acid metabolism, increases immunity, and provides energy for muscle tissue, brain, and central nervous system. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
Human Endogenous Metabolite |
| In Vitro | The viability of both hiPSCs, 201B7 cells and ehiPSCs decrease with an increase in L-Alanine concentration, and reach 7.5±1.3% and 3.7±0.7% respectively at 1.2 M of L-Alanine. On the other hand, no decrease in the viability of hFBs and hSkMCs are observed. Although the viability of iCMs slightly decreases along with the increase of the L-Alanine concentration, viability of iCMs at 1.2 M concentration of L-Alanine, 49.4±6.9%, is significantly higher than that of undifferentiated iPSCs, 201B7 cells and ehiPSCs (p< 0.01). The viability of hiPSCs, 201B7 cells and ehiPSCs, drastically decrease even after 2 or 4 h treatment. In contrast, the viability of hFBs fails to decrease at 1, 2, and 4 h and shows a small decrease at 24 h treatment. The viability of 201B7 cells in suspension culture decreases to 11.8±6.0% following treatment with 1.2 M L-Alanine for 2 h, whereas that of hFBs is 72.9±14.2%[1]. |
| Cell Assay | To investigate the selective removal of hiPSCs from differentiated cells by the high L-Alanine medium, two types of hiPSCs, 201B7 hiPSCs (201B7 cells) and an hiPSC line derived by episomal system (ehiPSCs) are used, along with normal human dermal fibroblasts (hFBs), human skeletal muscle cells (hSkMCs) and hiPSC-derived cardiomyocytes (iCMs) as differentiated cells. The cells are incubated in a medium supplemented with L-Alanine at various concentrations (0-1.2 M) or treatment times (1-24 h). The medium is replaced with a normal medium and the relative cell viability is measured after 24 h[1]. |
| References |
| Density | 1.2±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 212.9±23.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 314.5 °C (dec.)(lit.) |
| Molecular Formula | C3H7NO2 |
| Molecular Weight | 89.093 |
| Flash Point | 82.6±22.6 °C |
| Exact Mass | 89.047676 |
| PSA | 63.32000 |
| LogP | -0.68 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.1±0.9 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.460 |
| InChIKey | QNAYBMKLOCPYGJ-REOHCLBHSA-N |
| SMILES | CC(N)C(=O)O |
| Water Solubility | 166.5 g/L (25 ºC) |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATAMUTATION DATA
|
| Personal Protective Equipment | Eyeshields;Gloves;type N95 (US);type P1 (EN143) respirator filter |
|---|---|
| Hazard Codes | Xi: Irritant; |
| Risk Phrases | 36/37/38 |
| Safety Phrases | S24/25 |
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
| RTECS | AY2990000 |
| HS Code | 2930901000 |
| Precursor 7 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 10 | |
| HS Code | 2930901000 |
|---|
|
Urinary metabolic fingerprinting of mice with diet-induced metabolic derangements by parallel dual secondary column-dual detection two-dimensional comprehensive gas chromatography.
J. Chromatogr. A. 1361 , 265-76, (2014) This study investigates the potential of a parallel dual secondary column-dual detection two-dimensional comprehensive GC platform (GC×2GC-MS/FID) for metabolic profiling and fingerprinting of mouse u... |
|
|
Inhaled lactonase reduces Pseudomonas aeruginosa quorum sensing and mortality in rat pneumonia.
PLoS ONE 9(10) , e107125, (2014) The effectiveness of antibiotic molecules in treating Pseudomonas aeruginosa pneumonia is reduced as a result of the dissemination of bacterial resistance. The existence of bacterial communication sys... |
|
|
Abiogenic Syntheses of Lipoamino Acids and Lipopeptides and their Prebiotic Significance.
Orig. Life Evol. Biosph. 45 , 427-37, (2015) Researchers have formed peptide bonds under a variety of presumed prebiotic conditions. Here it is proposed that these same conditions would have also formed amide bonds between fatty acids and amino ... |
| L-ARANINE |
| MFCD00064410 |
| Fmoc-L-Ala-OH |
| H-L-ALA-OH |
| H-ALA-OH |
| L-ALA |
| ALANINE |
| ALA |
| L-Alanine |
| Alanin |
| EINECS 200-273-8 |
| Ritalanine |
| L-alamine |
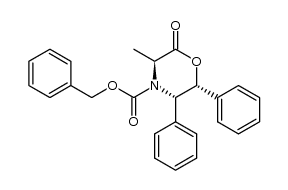 CAS#:100516-58-3
CAS#:100516-58-3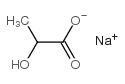 CAS#:312-85-6
CAS#:312-85-6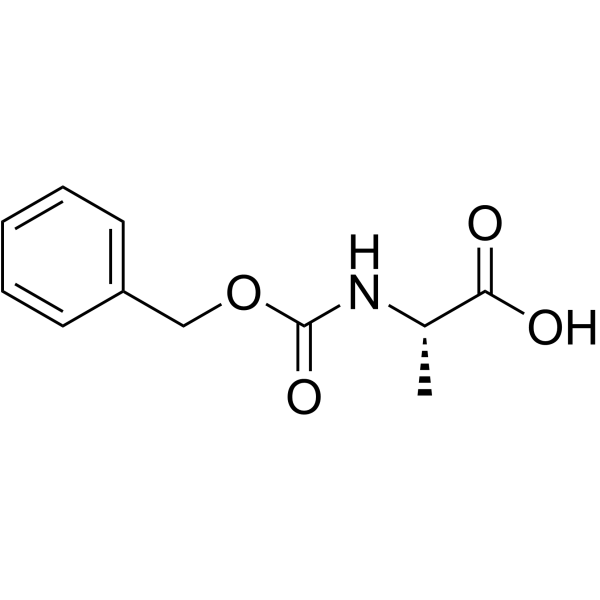 CAS#:1142-20-7
CAS#:1142-20-7 CAS#:136440-35-2
CAS#:136440-35-2 CAS#:504-07-4
CAS#:504-07-4 CAS#:21028-15-9
CAS#:21028-15-9![3-chloro-N-[3-(4-ethoxyphenoxy)-5-nitrophenyl]-5-thiophen-2-yl-7-(trifluoromethyl)pyrazolo[1,5-a]pyrimidine-2-carboxamide Structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/490/5673-65-4.png) CAS#:5673-65-4
CAS#:5673-65-4 CAS#:108462-95-9
CAS#:108462-95-9 CAS#:5625-46-7
CAS#:5625-46-7 CAS#:3303-34-2
CAS#:3303-34-2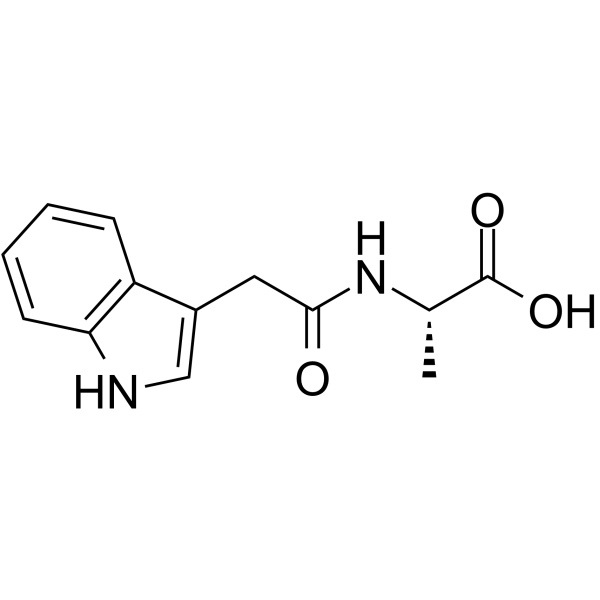 CAS#:57105-39-2
CAS#:57105-39-2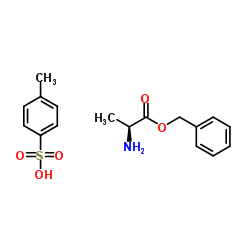 CAS#:42854-62-6
CAS#:42854-62-6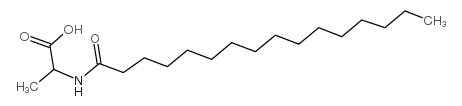 CAS#:56255-31-3
CAS#:56255-31-3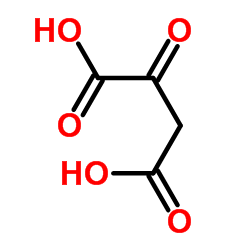 CAS#:328-42-7
CAS#:328-42-7 CAS#:32644-15-8
CAS#:32644-15-8 CAS#:39825-33-7
CAS#:39825-33-7 CAS#:56452-52-9
CAS#:56452-52-9
