| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
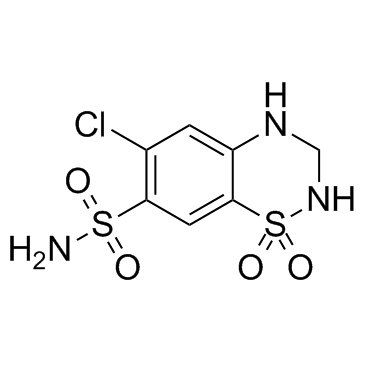 |
Hydrochlorothiazide
CAS:58-93-5 |
|
 |
Piroxicam
CAS:36322-90-4 |
|
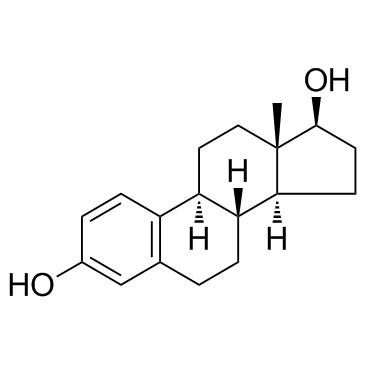 |
beta-Estradiol
CAS:50-28-2 |
|
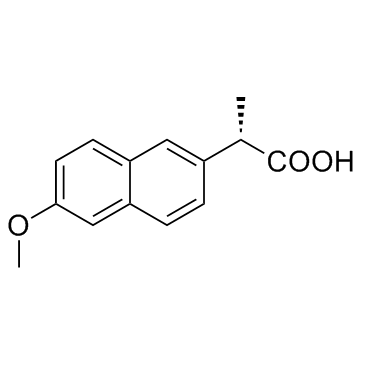 |
Naproxen
CAS:22204-53-1 |
|
 |
L-Nicotine
CAS:54-11-5 |
|
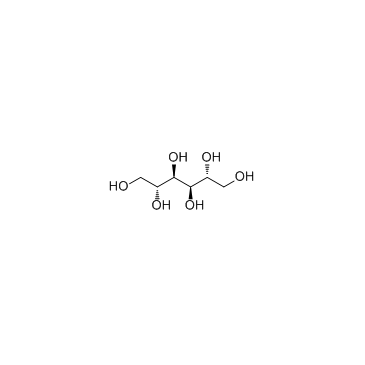 |
D-Mannitol
CAS:69-65-8 |
|
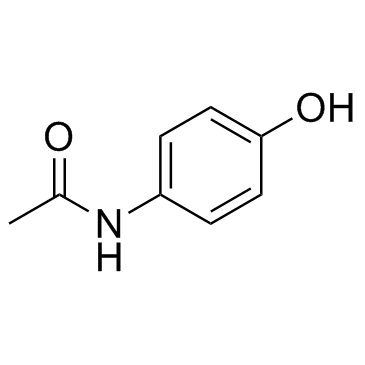 |
4-Acetamidophenol
CAS:103-90-2 |
|
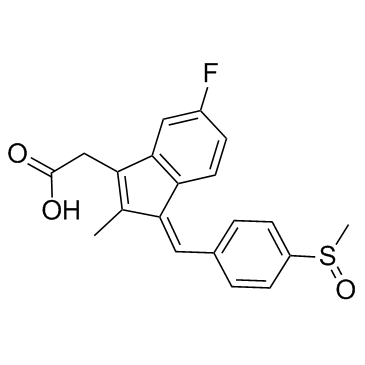 |
Sulindac
CAS:38194-50-2 |
|
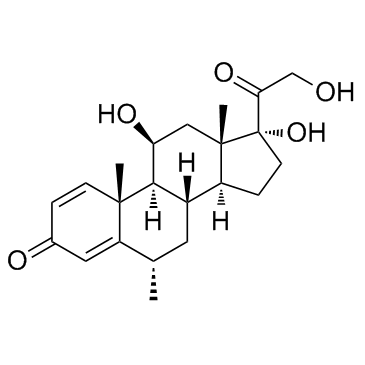 |
Methylprednisolone
CAS:83-43-2 |
|
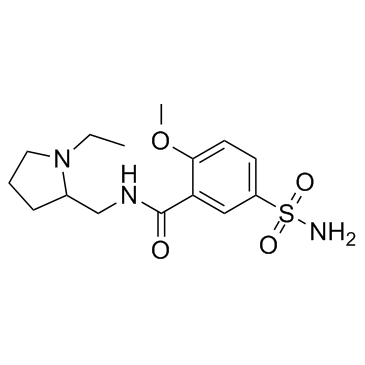 |
Sulpiride
CAS:15676-16-1 |