| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
Hydrochloric acid
CAS:7647-01-0 |
|
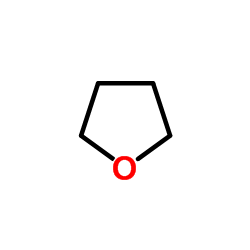 |
thf
CAS:109-99-9 |
|
 |
Ascorbic acid
CAS:50-81-7 |
|
 |
Sodium selenite
CAS:10102-18-8 |
|
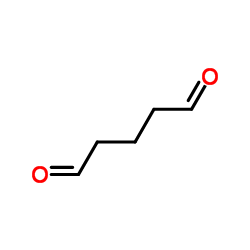 |
glutaraldehyde
CAS:111-30-8 |
|
 |
Dexamethasone
CAS:50-02-2 |
|
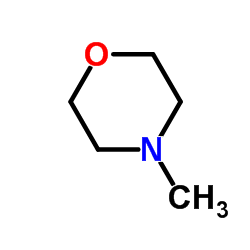 |
4-methylmorpholine
CAS:109-02-4 |
|
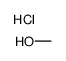 |
HYDROGEN CHLORIDE ~1.25 M IN METHANOL, 250 ML
CAS:132228-87-6 |