| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
Hydrochloric acid
CAS:7647-01-0 |
|
 |
sodium chloride
CAS:7647-14-5 |
|
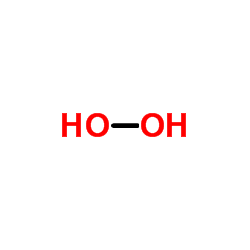 |
Hydrogen peroxide
CAS:7722-84-1 |
|
 |
Methanol
CAS:67-56-1 |
|
 |
Ascorbic acid
CAS:50-81-7 |
|
 |
Dimethyl sulfoxide
CAS:67-68-5 |
|
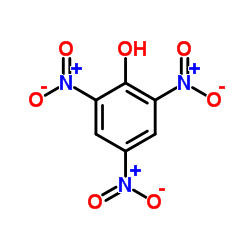 |
Trinitrophenol
CAS:88-89-1 |
|
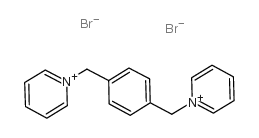 |
dpx
CAS:14208-10-7 |
|
 |
SODIUM CHLORIDE-35 CL
CAS:20510-55-8 |
|
 |
Hydrocortisone
CAS:50-23-7 |