| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
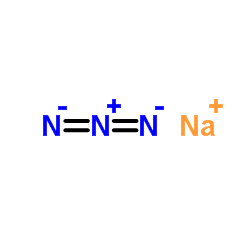 |
Sodium azide
CAS:26628-22-8 |
|
 |
Hydrochloric acid
CAS:7647-01-0 |
|
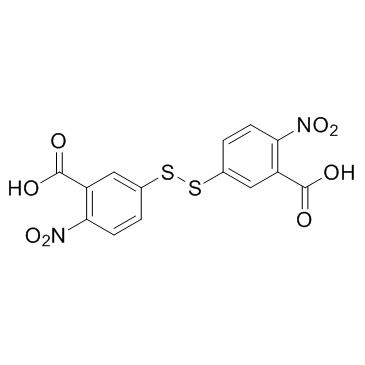 |
DTNB
CAS:69-78-3 |
|
 |
Dimethyl sulfoxide
CAS:67-68-5 |
|
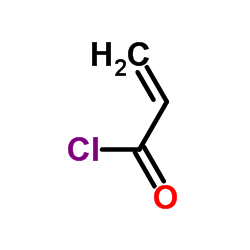 |
Acrylyl chloride
CAS:814-68-6 |
|
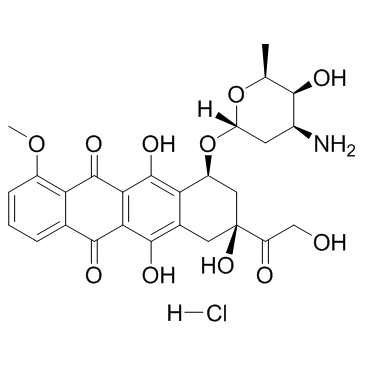 |
Doxorubicin Hydrochloride
CAS:25316-40-9 |
|
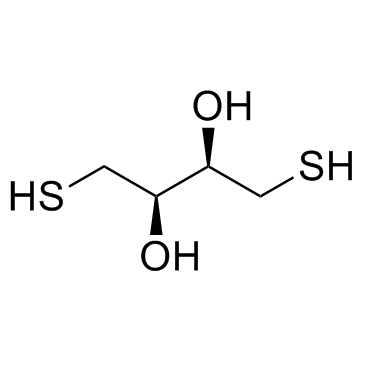 |
DL-Dithiothreitol
CAS:3483-12-3 |
|
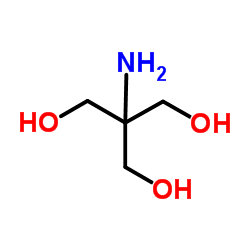 |
Trometamol
CAS:77-86-1 |
|
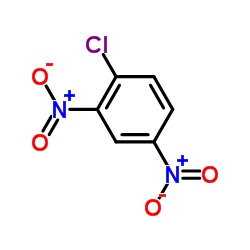 |
2,4-Dinitrochlorobenzene
CAS:97-00-7 |
|
 |
Glutathione
CAS:70-18-8 |