| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
Polymyxin B Sulfate
CAS:1405-20-5 |
|
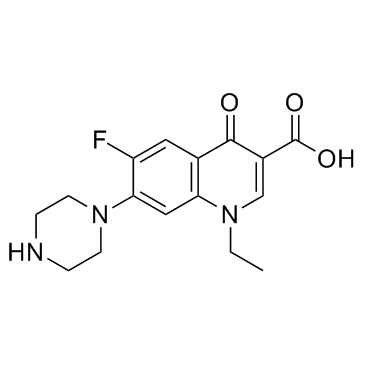 |
Norfloxacin
CAS:70458-96-7 |
|
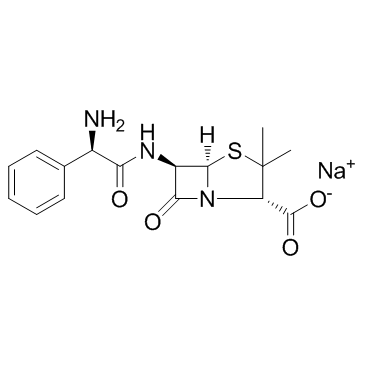 |
Ampicillin sodium
CAS:69-52-3 |
|
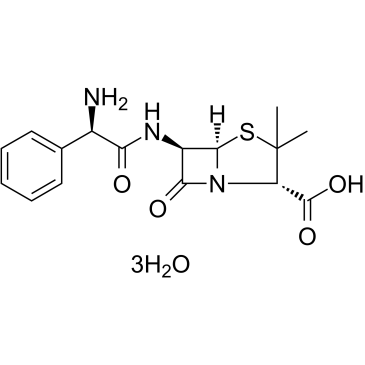 |
Ampicillin Trihydrate
CAS:7177-48-2 |
|
 |
Ampicillin
CAS:69-53-4 |