| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
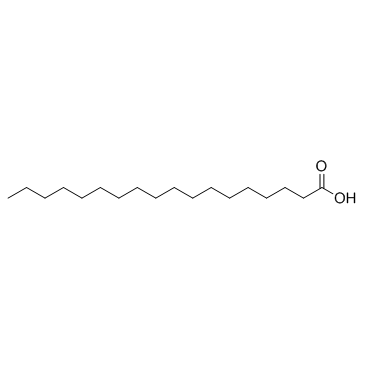 |
stearic acid
CAS:57-11-4 |
|
 |
Lactose
CAS:63-42-3 |
|
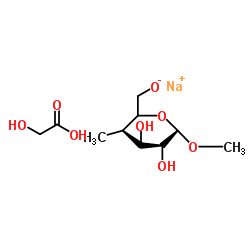 |
Sodium carboxyl methylstarch
CAS:9063-38-1 |