| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
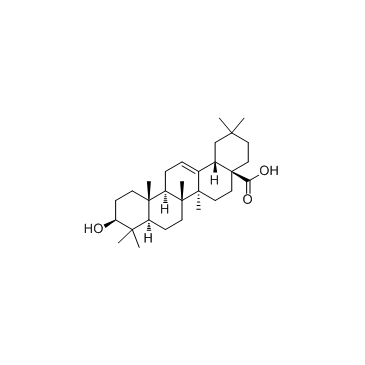 |
Oleanic acid
CAS:508-02-1 |
|
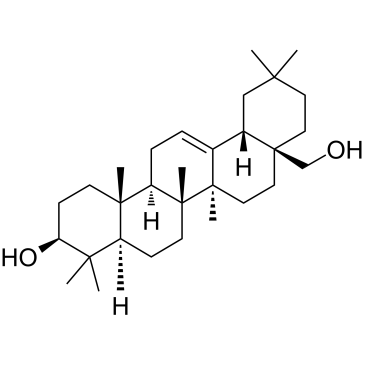 |
Erythrodiol
CAS:545-48-2 |
|
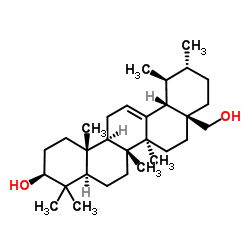 |
Uvaol
CAS:545-46-0 |
|
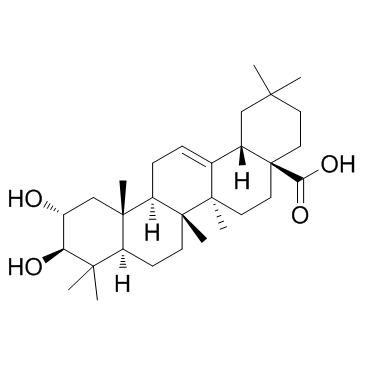 |
Crategolic acid
CAS:4373-41-5 |