| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
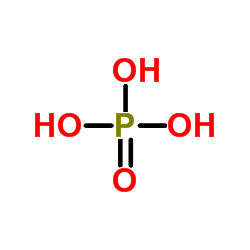 |
Phosphoric acid
CAS:7664-38-2 |
|
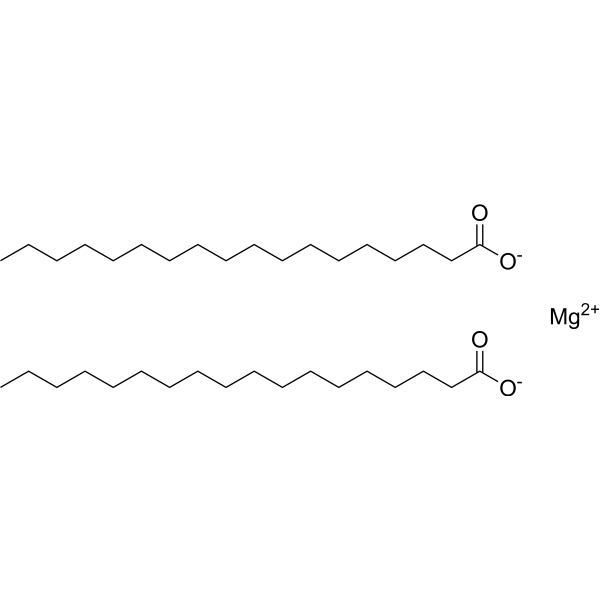 |
Magnesium stearate
CAS:557-04-0 |
|
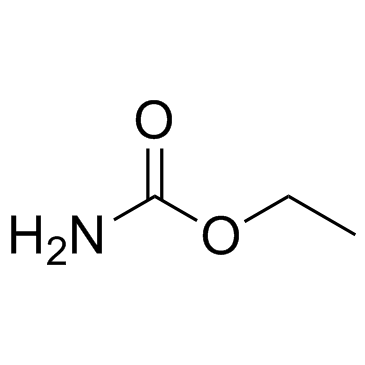 |
Urethane
CAS:51-79-6 |
|
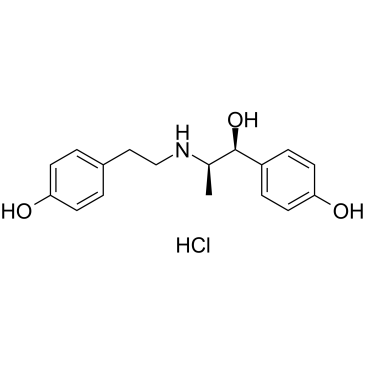 |
Ritodrine hydrochloride
CAS:23239-51-2 |