| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
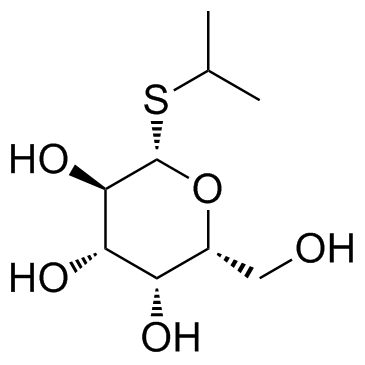 |
Isopropyl-beta-D-thiogalactopyranoside
CAS:367-93-1 |
|
 |
L-(+)-Lysine monohydrochloride
CAS:657-27-2 |
|
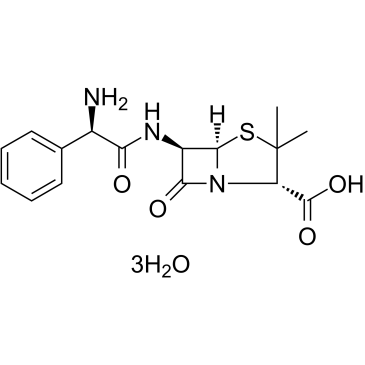 |
Ampicillin Trihydrate
CAS:7177-48-2 |
|
 |
Ampicillin
CAS:69-53-4 |
|
 |
4-Nitroanisole
CAS:100-17-4 |
|
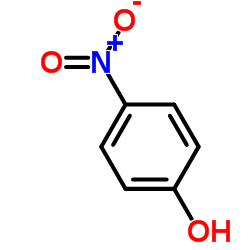 |
4-Nitrophenol
CAS:100-02-7 |