| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
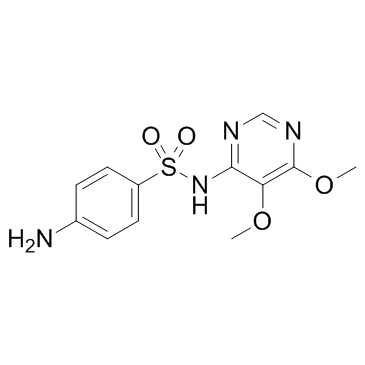 |
Sulfadoxine
CAS:2447-57-6 |
|
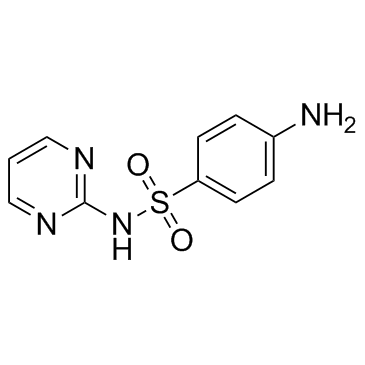 |
Sulfadiazine
CAS:68-35-9 |
|
 |
Oxazepam
CAS:604-75-1 |
|
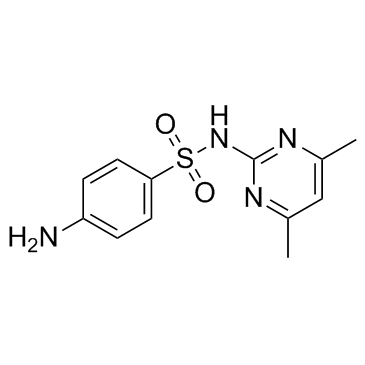 |
Sulfamethazine
CAS:57-68-1 |
|
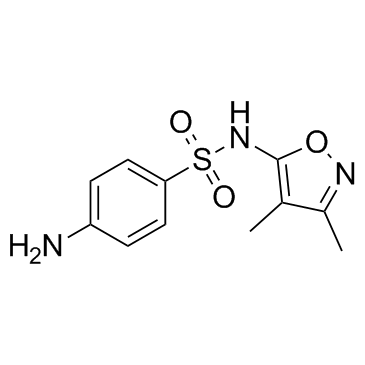 |
Sulfisoxazole
CAS:127-69-5 |
|
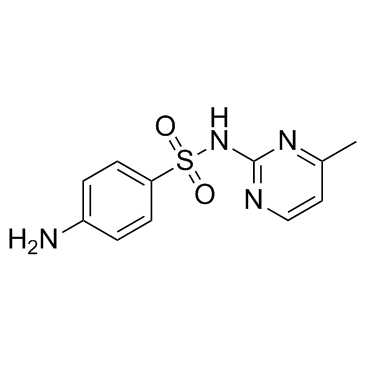 |
Sulfamerazine
CAS:127-79-7 |
|
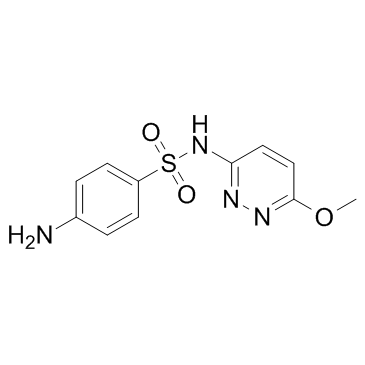 |
Sulfamethoxypyridazine
CAS:80-35-3 |
|
 |
Sulfameter
CAS:651-06-9 |
|
 |
temazepam
CAS:846-50-4 |
|
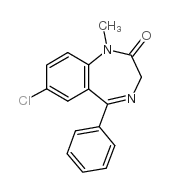 |
diazepam
CAS:439-14-5 |