| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
L-cysteine
CAS:52-90-4 |
|
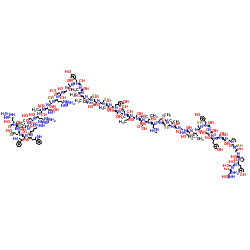 |
Epidermal Growth Factor (from mouse)
CAS:62229-50-9 |
|
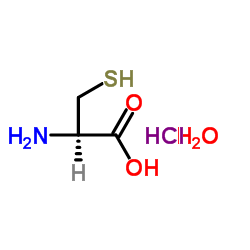 |
L-Cysteine hydrochloride hydrate
CAS:7048-04-6 |
|
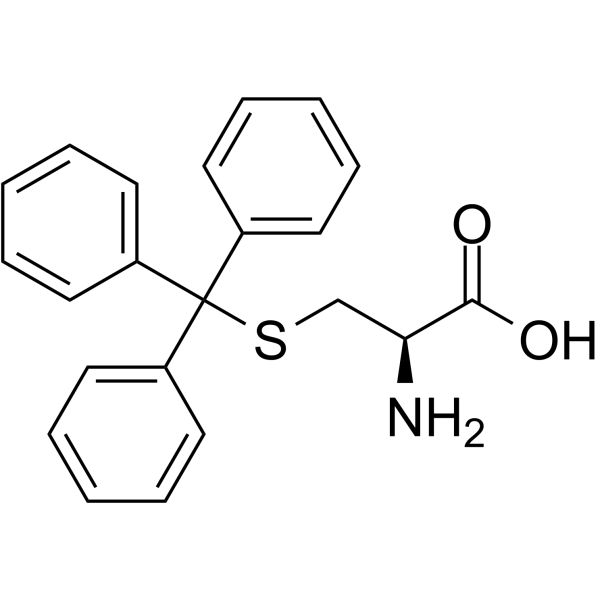 |
S-Tritylcysteine
CAS:2799-07-7 |